intro to psychophysical methods
Bonnie Cooper
Psychophysical Methodology
Psychophysics:
quantifying a relationship between stimulus & perception
Psychophysical Methodology
- Thresholds
- The Psychometric Function
- Methods for determining Thresholds
- Signal Detection Theory
- Weber's Law
Revisit the Photopic Luminosity Function

Thresholds
threshold - minimum quantity of the stimulus that can be detected or discriminated

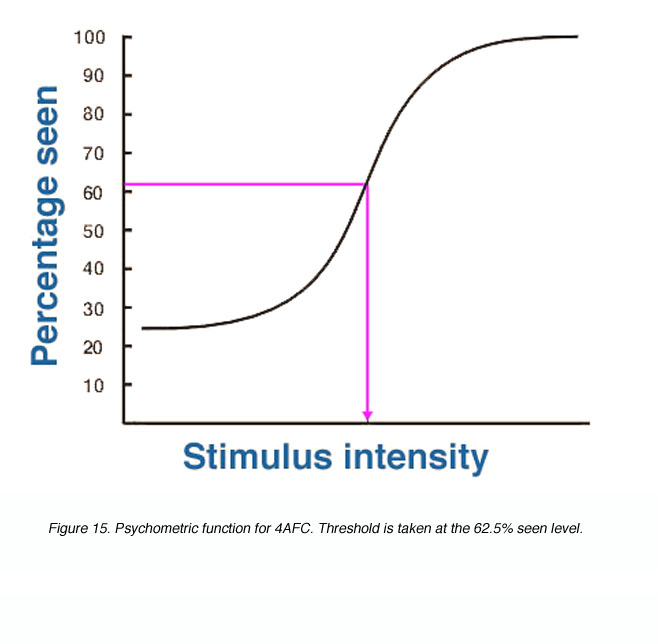
Psychometric Function
Psychophysical Methodology
- Method of Adjustment
- Method of Ascending Limits
- Method of Descending Limits
- Staircase Methods
- Method of Constant Stimuli
Method of Adjustment
- The stimulus intensity is adjusted to threshold by the observer
- Generally repeat each measurement several times & the threshold is taken as the average
- PROS: very fast!
- CONS: entirely up to the subject to set criterion & find threshold.
Method of (Ascending | Descending ) Limits
- Ascending: The stimulus intensity is gradually increased & the subject indicates if it is present or not
- Descending: The stimulus intensity is gradually decreased & the subject indicates if it is present or not. (Very common in clinic: e.g. Snellen acuity test.)
- Generally repeat each set several times & the threshold is taken as the average
- PROS: great for sensitive adaptation states.
- CONS: the subject's anticipation can influence thresholds

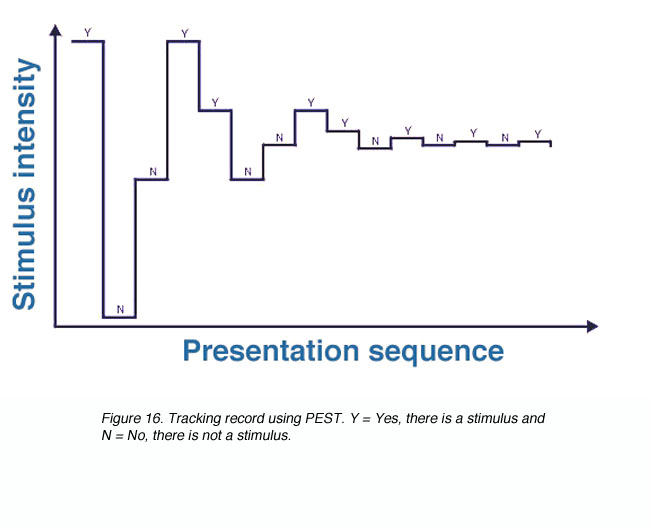
Adaptive Methods: Staircases
- Staircases generally starts well above threshold and turns 'corners' when the stimulus is either just subthreshold or just above.
- Generally repeat each staircase several times. The threshold for one staircase is taken as the average of the last several corners of the staircase.
- PROS: very thorough & flexible. Investigator can design the # of corners, size of steps etc.
- CONS: the subject's anticipation can still influence thresholds.
Method of Constant Stimuli
- MoCS takes a range of stimulus intensity values and randomly shuffles them
- Trials with no stimuli present allow the investigator to measure false positive rates
- A psychometric function can be build &threshold is generally taken where 50% chance detection takes place
- PROS: a false positive measure is informative of the subjects criterion. The subjects anticipation does not have as strong an effect as the previous methods
- CONS: for this & all the previous methods, the subjects criteria may drift during the experiments or between blocks of data collection

Forced Choice Methods: 2AFC, nAFC
- n alternatives are presented. The subject must chose which the stimulus was presented in
- may be spatial or temporal intervals

Psychometric Functions

Different psychophysical methods can be used to build psychometric functions that describe the same process
As is the case with the human Photopic Luminosity Function (Lennie et al 1993)
Introduction to Signal Detection Theory

Signal Detection Theory & Psychophysics

Detecting a Signal Against Noise
Signal: is there an enemy aircraft?
Decision: Should I raise an alarm
Signal: is there a stimulus present?
Decision: Should I indicate that I saw the stimulus?
Detecting a Signal Against Noise

Reciever Operator Characteristic
Weber's Law


“In order that the intensity of a sensation may increase in arithmetical progression, the stimulus must increase in geometrical progression.”