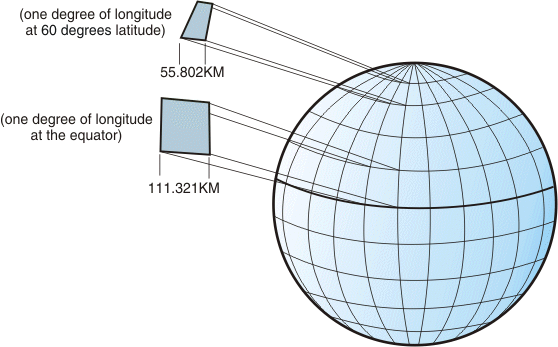
CRAN task view for spatial data:
https://cran.r-project.org/web/views/Spatial.html
Geocomputation with R:
https://geocompr.robinlovelace.net
sf package cheatsheet:
https://github.com/rstudio/cheatsheets/blob/master/sf.pdf
sf package overview:
https://r-spatial.github.io/sf/articles/sf1.html