R basics
Farid FLICI
18-05-2020
Algerian R Users Group
Plan
- Data manipulation
- Data visualization
- Editing (R markdown)
Plan
Data manipulation
- Data Structures: vector of characters, matrix, datafram
- c(), re(), seq(), matrix(), data.frame()
- t(), melt(), merge()
- for (), if(), ifelse()
Data visualization
- plot(), lines(), points
- barplot()
Editing (R markdown)
- Installing R markdown,
- writing text,
- Equations, figures, tables
Data structures
a vector
c(1, 3, 4, 5, 6)
[1] 1 3 4 5 6
a sequence
seq(1, 9, by=1)
[1] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
seq(1, 9, by=1)+3
[1] 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
Data structures
a repitition
rep(5, 6)
[1] 5 5 5 5 5 5
rep(NA, 6)
[1] NA NA NA NA NA NA
Data structures
a matrix
M <- matrix(c(1:20), byrow=T, ncol=5)
M
[,1] [,2] [,3] [,4] [,5]
[1,] 1 2 3 4 5
[2,] 6 7 8 9 10
[3,] 11 12 13 14 15
[4,] 16 17 18 19 20
N <- matrix(c(1:20), byrow=F, ncol=5)
N
[,1] [,2] [,3] [,4] [,5]
[1,] 1 5 9 13 17
[2,] 2 6 10 14 18
[3,] 3 7 11 15 19
[4,] 4 8 12 16 20
Data structures
a vector
M1 <- matrix(seq(18,20), ncol=1)
M1
[,1]
[1,] 18
[2,] 19
[3,] 20
N1 <- matrix(seq(16,18), nrow=1)
N1
[,1] [,2] [,3]
[1,] 16 17 18
Data structures
vectors
M2 <- M1+1
M2
[,1]
[1,] 19
[2,] 20
[3,] 21
N2 <- N1*3
N2
[,1] [,2] [,3]
[1,] 48 51 54
Data structures
M1
[,1]
[1,] 18
[2,] 19
[3,] 20
N1
[,1] [,2] [,3]
[1,] 16 17 18
M1%*%N1
[,1] [,2] [,3]
[1,] 288 306 324
[2,] 304 323 342
[3,] 320 340 360
N1%*%M1
[,1]
[1,] 971
Data structures
Matrices subsetting
M
[,1] [,2] [,3] [,4] [,5]
[1,] 1 2 3 4 5
[2,] 6 7 8 9 10
[3,] 11 12 13 14 15
[4,] 16 17 18 19 20
M[, -1]
[,1] [,2] [,3] [,4]
[1,] 2 3 4 5
[2,] 7 8 9 10
[3,] 12 13 14 15
[4,] 17 18 19 20
Data structures
Matrices subsetting
M
[,1] [,2] [,3] [,4] [,5]
[1,] 1 2 3 4 5
[2,] 6 7 8 9 10
[3,] 11 12 13 14 15
[4,] 16 17 18 19 20
M[, c(-1,-2)]
[,1] [,2] [,3]
[1,] 3 4 5
[2,] 8 9 10
[3,] 13 14 15
[4,] 18 19 20
M[-2,]
[,1] [,2] [,3] [,4] [,5]
[1,] 1 2 3 4 5
[2,] 11 12 13 14 15
[3,] 16 17 18 19 20
Data structures
Matrices subsetting
M
[,1] [,2] [,3] [,4] [,5]
[1,] 1 2 3 4 5
[2,] 6 7 8 9 10
[3,] 11 12 13 14 15
[4,] 16 17 18 19 20
subset(M, select=c(1:3))
[,1] [,2] [,3]
[1,] 1 2 3
[2,] 6 7 8
[3,] 11 12 13
[4,] 16 17 18
M[3:4, 3:5]
[,1] [,2] [,3]
[1,] 13 14 15
[2,] 18 19 20
Useful R functions
rbind(), cbind()
add some columns
M
[,1] [,2] [,3] [,4] [,5]
[1,] 1 2 3 4 5
[2,] 6 7 8 9 10
[3,] 11 12 13 14 15
[4,] 16 17 18 19 20
M4 <- cbind(M, rep(1, nrow(M)))
M4
[,1] [,2] [,3] [,4] [,5] [,6]
[1,] 1 2 3 4 5 1
[2,] 6 7 8 9 10 1
[3,] 11 12 13 14 15 1
[4,] 16 17 18 19 20 1
Useful R functions
rbind(), cbind()
add some columns
M
[,1] [,2] [,3] [,4] [,5]
[1,] 1 2 3 4 5
[2,] 6 7 8 9 10
[3,] 11 12 13 14 15
[4,] 16 17 18 19 20
M5 <- cbind(M, matrix(rep(1), ncol=2, nrow=nrow(M)))
M5
[,1] [,2] [,3] [,4] [,5] [,6] [,7]
[1,] 1 2 3 4 5 1 1
[2,] 6 7 8 9 10 1 1
[3,] 11 12 13 14 15 1 1
[4,] 16 17 18 19 20 1 1
Useful R functions
rbind(), cbind()
add some rows
M
[,1] [,2] [,3] [,4] [,5]
[1,] 1 2 3 4 5
[2,] 6 7 8 9 10
[3,] 11 12 13 14 15
[4,] 16 17 18 19 20
M6 <- rbind(M, rep(1, ncol(M)))
M6
[,1] [,2] [,3] [,4] [,5]
[1,] 1 2 3 4 5
[2,] 6 7 8 9 10
[3,] 11 12 13 14 15
[4,] 16 17 18 19 20
[5,] 1 1 1 1 1
Useful R functions
rbind(), cbind()
add some rows
M
[,1] [,2] [,3] [,4] [,5]
[1,] 1 2 3 4 5
[2,] 6 7 8 9 10
[3,] 11 12 13 14 15
[4,] 16 17 18 19 20
M7 <- rbind(M, matrix(rep(1), nrow=2, ncol=ncol(M)))
M7
[,1] [,2] [,3] [,4] [,5]
[1,] 1 2 3 4 5
[2,] 6 7 8 9 10
[3,] 11 12 13 14 15
[4,] 16 17 18 19 20
[5,] 1 1 1 1 1
[6,] 1 1 1 1 1
Useful R functions
subsetting
Example: form “M”, select only the “rows” having a value “>=” to “10” within columns “5”.
M
[,1] [,2] [,3] [,4] [,5]
[1,] 1 2 3 4 5
[2,] 6 7 8 9 10
[3,] 11 12 13 14 15
[4,] 16 17 18 19 20
M[ M[ , 5]>=10, ]
[,1] [,2] [,3] [,4] [,5]
[1,] 6 7 8 9 10
[2,] 11 12 13 14 15
[3,] 16 17 18 19 20
Useful R functions
subsetting
Select only columns 3,
M[ M[ , 5]>=10, 3]
[1] 8 13 18
length(M[ M[ , 5]>=10, 3])
[1] 3
Useful R functions
for() and if()
in M, we replace the values M[ ,2] <=10 by 10.
Ma <- M
Ma[ Ma[ ,2]<=10,2]<-rep(10,length(Ma[Ma[,2]<=10,2]))
Ma
[,1] [,2] [,3] [,4] [,5]
[1,] 1 10 3 4 5
[2,] 6 10 8 9 10
[3,] 11 12 13 14 15
[4,] 16 17 18 19 20
or
Mb<-M
for (i in 1: nrow(Mb)){ if(Mb[i,2]<=10){Mb[i, 2]<-10} }
Mb
[,1] [,2] [,3] [,4] [,5]
[1,] 1 10 3 4 5
[2,] 6 10 8 9 10
[3,] 11 12 13 14 15
[4,] 16 17 18 19 20
Useful R functions
melt() and cast()
for example, we have a matrix \( tax \), indicating tax amount (in cells) for car by power (column) and year (rows)
tax<- matrix(seq(1000, 15000, by=1000 ), byrow = T, ncol=5)
colnames(tax)<-seq(2011, 2015)
rownames(tax)<-c(4,5,7)
tax
2011 2012 2013 2014 2015
4 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000
5 6000 7000 8000 9000 10000
7 11000 12000 13000 14000 15000
Useful R functions
melt()
melt() allows to rewrite the matrix into 3 columns dataframe (power, year, tax)
library(reshape2)
tax2<-melt(tax)
colnames(tax2)<-c("power", "year", "tax")
tax2
power year tax
1 4 2011 1000
2 5 2011 6000
3 7 2011 11000
4 4 2012 2000
5 5 2012 7000
6 7 2012 12000
7 4 2013 3000
8 5 2013 8000
9 7 2013 13000
10 4 2014 4000
11 5 2014 9000
12 7 2014 14000
13 4 2015 5000
14 5 2015 10000
15 7 2015 15000
Useful R functions
cast()
cast() allows aggregating data, it is the adverse function for melt()
library(reshape2)
head(tax2)
power year tax
1 4 2011 1000
2 5 2011 6000
3 7 2011 11000
4 4 2012 2000
5 5 2012 7000
6 7 2012 12000
dcast(tax2, power~year, mean)
power 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015
1 4 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000
2 5 6000 7000 8000 9000 10000
3 7 11000 12000 13000 14000 15000
We replace “mean” by “length” if we want to have counts on “cells”
Useful R functions
Examples
We create two dataframes
A <- data.frame(ID=seq(1,10), Age=c(15, 24, 32, 18, 46, 35, 38, 34, 46, 42), sex=c(1, 2, 2, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 1, 2), chl=c(0, 1, 2, 0, 3, 1, 2, 3, 2, 0))
B<- data.frame(ID=seq(6,15), wrk=c(1, 1, 0, 1,1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0), std=c(1,1,2,2,3,3,4,4, 3, 2))
A
ID Age sex chl
1 1 15 1 0
2 2 24 2 1
3 3 32 2 2
4 4 18 1 0
5 5 46 1 3
6 6 35 1 1
7 7 38 2 2
8 8 34 2 3
9 9 46 1 2
10 10 42 2 0
Examples
A <- data.frame(ID=seq(1,10), Age=c(15, 24, 32, 18, 46, 35, 38, 34, 46, 42), sex=c(1, 2, 2, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 1, 2), chl=c(0, 1, 2, 0, 3, 1, 2, 3, 2, 0))
B<- data.frame(ID=seq(6,15), wrk=c(1, 1, 0, 1,1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0), std=c(1,1,2,2,3,3,4,4, 3, 2))
cbind.data.frame(A,"---"=rep("---"), B)
ID Age sex chl --- ID wrk std
1 1 15 1 0 --- 6 1 1
2 2 24 2 1 --- 7 1 1
3 3 32 2 2 --- 8 0 2
4 4 18 1 0 --- 9 1 2
5 5 46 1 3 --- 10 1 3
6 6 35 1 1 --- 11 0 3
7 7 38 2 2 --- 12 0 4
8 8 34 2 3 --- 13 1 4
9 9 46 1 2 --- 14 1 3
10 10 42 2 0 --- 15 0 2
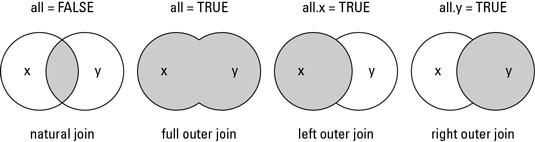
Different ways to merge A and B
Inner Join
C<-merge(x=A, y=B, by="ID", all=FALSE)
C
ID Age sex chl wrk std
1 6 35 1 1 1 1
2 7 38 2 2 1 1
3 8 34 2 3 0 2
4 9 46 1 2 1 2
5 10 42 2 0 1 3
Different ways to merge A and B
left Join
D<-merge(x=A, y=B, by="ID", all.x=TRUE)
D
ID Age sex chl wrk std
1 1 15 1 0 NA NA
2 2 24 2 1 NA NA
3 3 32 2 2 NA NA
4 4 18 1 0 NA NA
5 5 46 1 3 NA NA
6 6 35 1 1 1 1
7 7 38 2 2 1 1
8 8 34 2 3 0 2
9 9 46 1 2 1 2
10 10 42 2 0 1 3
Different ways to merge A and B
Right Join
E<-merge(x=A, y=B, by="ID", all.y=TRUE)
E
ID Age sex chl wrk std
1 6 35 1 1 1 1
2 7 38 2 2 1 1
3 8 34 2 3 0 2
4 9 46 1 2 1 2
5 10 42 2 0 1 3
6 11 NA NA NA 0 3
7 12 NA NA NA 0 4
8 13 NA NA NA 1 4
9 14 NA NA NA 1 3
10 15 NA NA NA 0 2
Different ways to merge A and B
Outer (full) Join
G<-merge(x=A, y=B, by="ID", all.x=TRUE, all.y=TRUE)
G
ID Age sex chl wrk std
1 1 15 1 0 NA NA
2 2 24 2 1 NA NA
3 3 32 2 2 NA NA
4 4 18 1 0 NA NA
5 5 46 1 3 NA NA
6 6 35 1 1 1 1
7 7 38 2 2 1 1
8 8 34 2 3 0 2
9 9 46 1 2 1 2
10 10 42 2 0 1 3
11 11 NA NA NA 0 3
12 12 NA NA NA 0 4
13 13 NA NA NA 1 4
14 14 NA NA NA 1 3
15 15 NA NA NA 0 2
Useful R functions
gather() and spread()
library(tidyr)
tab <- data.frame( year=c(2000,2010,2020),Alg=c(40,50,60),
Tun=c(10,15,25),Mor=c(17,19,21) )
tab
year Alg Tun Mor
1 2000 40 10 17
2 2010 50 15 19
3 2020 60 25 21
tab1<-gather(tab,"country","pop",Alg:Mor)
tab1
year country pop
1 2000 Alg 40
2 2010 Alg 50
3 2020 Alg 60
4 2000 Tun 10
5 2010 Tun 15
6 2020 Tun 25
7 2000 Mor 17
8 2010 Mor 19
9 2020 Mor 21
Useful R functions
gather() and spread()
library(tidyr)
tab2<-spread(tab1,key="year",value="pop")
tab2
country 2000 2010 2020
1 Alg 40 50 60
2 Mor 17 19 21
3 Tun 10 15 25
tab2<-spread(tab1,key="country",value="pop")
tab2
year Alg Mor Tun
1 2000 40 17 10
2 2010 50 19 15
3 2020 60 21 25
Useful R functions
separate() and unite()
serial <- data.frame(
ID=seq(100,105),Dep=c(20,35,16,18,40,21),
srl_num=c(11421,11643,11322,13243,23432,44354),
ybirth=c("1970","1987","1994","1970","1987","1994"),
mbirth=c(4,12,1,5,7,3),dbirth=c(12,21,24,4,12,6)
)
serial
ID Dep srl_num ybirth mbirth dbirth
1 100 20 11421 1970 4 12
2 101 35 11643 1987 12 21
3 102 16 11322 1994 1 24
4 103 18 13243 1970 5 4
5 104 40 23432 1987 7 12
6 105 21 44354 1994 3 6
Useful R functions
separate() and unite()
# separate the serial number into 2 sub-codes separated by the 3rd character
serial1<-separate(serial,srl_num,c("#1","#2"),sep=3)
serial1
ID Dep #1 #2 ybirth mbirth dbirth
1 100 20 114 21 1970 4 12
2 101 35 116 43 1987 12 21
3 102 16 113 22 1994 1 24
4 103 18 132 43 1970 5 4
5 104 40 234 32 1987 7 12
6 105 21 443 54 1994 3 6
Useful R functions
separate() and unite()
serial
ID Dep srl_num ybirth mbirth dbirth
1 100 20 11421 1970 4 12
2 101 35 11643 1987 12 21
3 102 16 11322 1994 1 24
4 103 18 13243 1970 5 4
5 104 40 23432 1987 7 12
6 105 21 44354 1994 3 6
serial2<-unite_(serial,"date_birth",c("ybirth","mbirth","dbirth"), sep="-")
serial2
ID Dep srl_num date_birth
1 100 20 11421 1970-4-12
2 101 35 11643 1987-12-21
3 102 16 11322 1994-1-24
4 103 18 13243 1970-5-4
5 104 40 23432 1987-7-12
6 105 21 44354 1994-3-6
Some Free Courses
Some Free Courses
GLM modeling https://learn.datacamp.com/courses/generalized-linear-models-in-r
Joining Data with dplyr (datacamp course) https://learn.datacamp.com/courses/joining-data-with-dplyr-b3f91a4a-4a9d-4a6f-b655-292a1641c3e2
DataVis with R https://learn.datacamp.com/courses/data-visualization-in-r
Introduction to DataViz with ggplot2: https://learn.datacamp.com/courses/introduction-to-data-visualization-with-ggplot2
forecasting R https://learn.datacamp.com/courses/forecasting-in-r
Some Free Courses
Spatial Analysis https://learn.datacamp.com/courses/spatial-statistics-in-r
Survival analysis https://learn.datacamp.com/courses/survival-analysis-in-r
Clinical Trial analysis https://learn.datacamp.com/courses/designing-and-analyzing-clinical-trials-in-r
Basic Plots with R
- plot()
- barplot()
- hist()
Basic Plots with R
plot(x=seq(1,10), y=c(10,4,15,25,5,3,16,1,30, 21))
lines(x=c(1,10),y=c(1,15) )
Basic Plots with R
barplot(c(10,4,15,25,5,3,16,1,30, 21), names.arg = c("a","b","c","d","e","f","g","h","i","j"), cex.axis=2, cex.names = 2 )
Basic Plots with R
hist(c(10,4,15,25,5,3,16,1,30))