Radiation Protection II
Sofia Skyttner, MSc
2019
Please, press F11 for full screen!
Who is here today?
Any question = good question!

 Ministry of Information Photo Devision Photographer
Ministry of Information Photo Devision Photographer
National Authority in Radiation Protection
Swedish Radiation Safety Authority
Strålsäkerhetsmyndigheten (SSM)
Strålskyddslagen (2018:396)
- 1 § Humans, animals and environment shall be protected to the harm of radiation
https://www.riksdagen.se/sv/dokument-lagar/dokument/svensk-forfattningssamling/stralskyddslag-2018396_sfs-2018-396
Strålskyddsförordning (2018:506)
Föreskrifter (SSM FS 2018-XX)
Strålskyddslagen (2018:396)
1 § Syftet med denna lag är att skydda människors hälsa och miljön mot skadlig verkan av strålning.
2 § Lagen är indelad i följande kapitel:
- 1 kap. Lagens syfte och innehåll
- 2 kap. Lagens tillämpningsområde
- 3 kap. Grundläggande bestämmelser om skydd mot joniserande strålning
- 4 kap. Arbetstagares exponering för joniserande strålning
- 5 kap. Allmänhetens och miljöns exponering för joniserande strålning
- 6 kap. Tillstånd och anmälan i fråga om joniserande strålning
- 7 kap. Tekniska anordningar som kan alstra icke-joniserande strålning
- 8 kap. Tillsyn
- 9 kap. Straff och förverkande
- 10 kap. Tystnadsplikt, överklagande och avgifter
Strålskyddsförordning (2018:506)
1 kap. Förordningens innehåll
2 kap. Dosgränser
3 kap. Optimering
4 kap. Andra bestämmelser om skydd mot strålning
5 kap. Tillstånd och anmälan
6 kap. Dokumentation, information och samtycke
7 kap. Andra bestämmelser om undantag och dispenser
8 kap. Tillsyn
9 kap. Straff, överklagande och verkställighet
Regulations of SSM
- SSMFS 2018:1 Strålsäkerhetsmyndighetens föreskrifter om grundläggande bestämmelser för tillståndspliktig verksamhet med joniserande strålning
- SSMFS 2018:2 Strålsäkerhetsmyndighetens föreskrifter om anmälningspliktiga verksamheter
- SSMFS 2018:5 Strålsäkerhetsmyndighetens föreskrifter och allmänna råd om medicinska exponeringar
- SSMFS 2018:9 Strålsäkerhetsmyndighetens föreskrifter om godkända persondosimetritjänster
- SSMFS 2014:4 Strålsäkerhetsmyndighetens föreskrifter och allmänna råd om laser, starka laserpekare och intensivt pulserat ljus
(FS = Föreskrift)
Read more: https://www.stralsakerhetsmyndigheten.se/omraden/stralning-i-varden/foreskrifter/?sort=date
Reports of SSM
- SSM Report 2009:03 National Survey on justification of CT examinations in Sweden
- SSM Report 2010:14 Patientdoser från röntgenundersökningar i Sverige (2005-2008)
- SSM Report 2012:23 Samlad strålsäkerhetsvärdering av hälso- och sjukvård
- SSM Report 2013:11 Mätmetoder för bestämning av stråldoser till ögats lins
International Organizations in Radiation Protection
UNSCEAR - United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation
Assess and report on levels and effects of ionizing radiation exposure
IAEA - International Atomic Energy Agency
Safety fundamentals, requirements, guides & practices
ICRP - International Commission on Radiological Protection
Providing recommendations and guidance on all aspects of (ionizing) radiation protection
Publications: http://www.icrp.org/publications.asp
Other international organizations
AAPM - American Association of Physicists in Medicine
RSNA - Radiological Society of North America
ACR - American College of Radiology
IRPA - International Radiation Protection Association
IPEM - Institute of Physics and Engineering in Medicine
…and many more!
Principles of Radiation Protection
Justification & Optimization
Justification & optimization
Toolkit to handle following issues
- Radiation safety authorities & organizations
- Protection quantities
- Risk: late and acute effects
- Distance, time & shielding
- Categorization of staff and rooms
- X-ray techniques that yield high doses
- Special patient subgroups
- Radiation related accidents & research
Patient of today...?



 紫流 (left)
紫流 (left)
All exams should be justified and optimized!
The principle of justification
X-rays in medical imaging should do more good than harm and
benefit-to-risk-ratio should be kept…
…As High As Reasonably Achievable (AHARA)
Individual (or societal) benefit should
be higher than the detriment it causes.
Read more: ICRP 103
The principle of optimization
Optimization is a cyclic multidisciplinary process primarily involving:
- Radiologist
- Radiographer
- Medical physicist
Without loosing diagnostics in image quality
patient dose should be kept…
…As Low As Reasonably Achievable (ALARA)
Choosing between image modalities, diagnostic tasks, optimization strategies & dose sparing techniques
Read more: ICRP 103
Radiation protection team work
Radiologist + medical physicist + radiographer + …



 Craig Taylor
Craig Taylor
… + surgeon + surgery nurse + medical engineer + contact person + radiation agent (strålskyddsombud) + remittent (regarding referals) + intensive care nurse + …
Radiation protection organization
Know YOUR who/what/when/how!
Radiation Protection Organization = Multiplication Table
How to assess risks related to medical X-rays?
Formal system for a feasible and structured approach to radiation protection!
To assess dose…
…use reference anatomical and physiological models of man
To assess hazards…
…use molecular and cellular studies
To assess probability of detriment…
…use animal experiments; epidemiology
Read more: ICRP 103
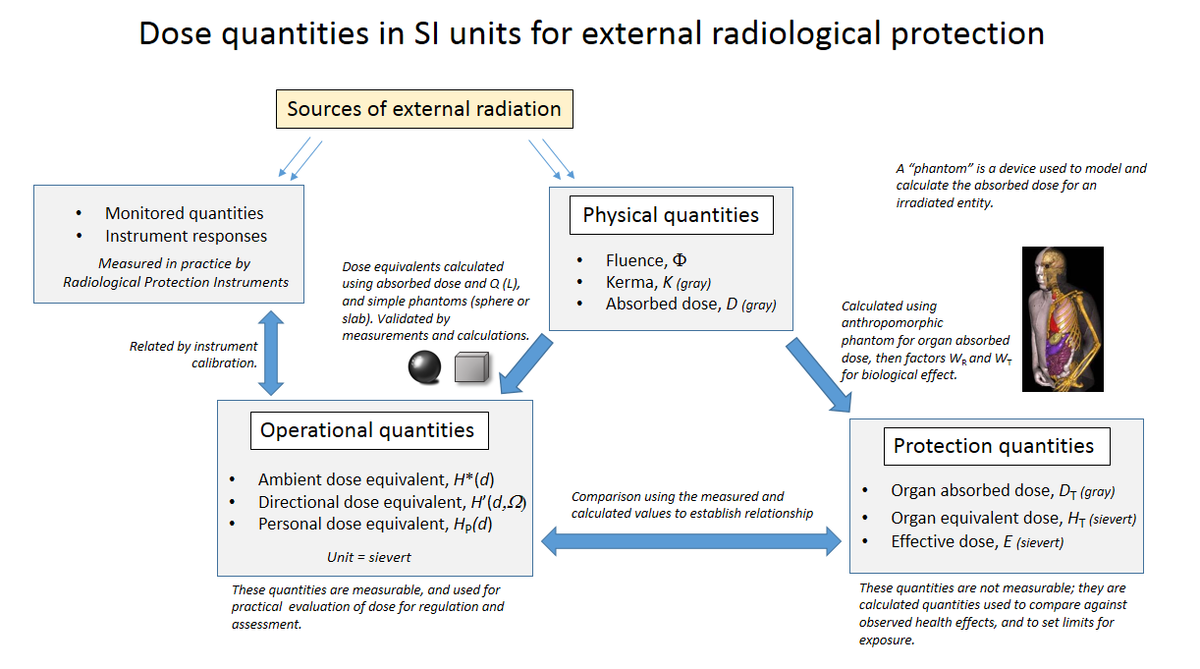
Radiation dose
Dose quantities
Stochastic effects – Late effects
The probability of the effect occurring,
increases with dose, but not its severity
Additive risk for cancer
At low doses...?
Contradictory results…!



 Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
B - the precautionary principle (försiktighetsprincipen)!
Read more: BIER VII Report
100 individuals exposed to 100 mSv...
Acute (deterministic) effects - staff



 Rakesh Ahuja, MD
Rakesh Ahuja, MD
Radiation induced catharact, equivalent dose > 0.5 Sv
The severity of the effect occurring increases with dose, but not its probability
SSM dose limits
Effective dose
- staff, 20 mSv/year
(patient family member: 1 mSv/year, patient: no dose limit)
Equivalent dose
- fetal dose, 1 mSv/pregnancy
- eye lens dose, 15 mSv/year
- skin & extremities, 500 mSv/year
Karolinska investigation limits
H_p(10)
- staff, 5 mSv/year (i.e. 0.5 mSv/month)
H_p(0.07)
- eye lens dose, 5 mSv/year (i.e. 0.5 mSv/month)
- skin & extremities, 50 mSv/year (i.e. 5 mSv/month)
Dosimeters: http://www.landauer.se/dosimetri-service/
Natural radiation: 1 mSv/year



 NASA Goddard Space Flight Center (left)
NASA Goddard Space Flight Center (left)
- Category B: supervised area (skyddat område)
- Category A: controlled area (kontrollerat område)
Upgrade to A-team...?
A (risk to exceed effective dose 6 mSv/year)
- Surgeons/radiologists/nurses (angio-/intervention)
B (risk to exceed effective dose 1 mSv/year)
- Nurses & physicians in anesthesia/intensive care
- Surgery nurses & surgeons (C-arm)
- Radiographers & radiologists (CT/conv X-ray)
- Biomedical scientists (pediatric angio)
- Engineers & medical physicists (all modalities)
Radiation protection dose quantities


 Sofia Skyttner
Sofia Skyttner
Example
CT head examination
- Absorbed dose to brain = 50 mGy
- Equivalent dose to brain = 50 mSv
- Effective dose for exam = 2 mSv
Radiation protection dose quantities
Most radiosensitive organs
| Organ | Tissue weighting factor |
|---|---|
| Breasts | 0.12 |
| Colon | 0.12 |
| Lung | 0.12 |
| Red Bone Marrow | 0.12 |
| Stomach | 0.12 |
| Gonads | 0.08 |
| Whole body | 1.00 |
Read more: ICRP 103 (2007)
Other radiosensitive organs
| Organ | Tissue weighting factor |
|---|---|
| Bladder | 0.04 |
| Liver | 0.04 |
| Oesophagus | 0.04 |
| Thyroid | 0.04 |
| Skin | 0.04 |
| Bone surface | 0.01 |
| Salivary glands | 0.01 |
| Brain | 0.01 |
| Remainder (*) | 0.12 |
(*) Adrenals, Extrathoracic region, Gall bladder, Heart, Kidneys, Lymphatic nodes, Muscle, Oral mucosa, Pancreas, Prostate (M), Small intestine, Spleen, Thymus, Uterus/cervix (F)
Read more: ICRP 103 (2007)
Effective dose – when and how?
Effective dose for comparing…
- …different diagnostic procedures
- …similar procedures in different hospitals and countries
- …different technologies for the same medical examination
Organ dose for…
- …detailed retrospective dose and risk assessments after exposure of individuals
- …epidemiological studies (i.e. study and analysis of the patterns, causes, and effects of ionizing radiation in defined populations)
- …accidents involving ionizing radiation
Reference level is NOT a dose limit
Diagnostic Standard Dose
- DSD, Diagnostisk standarddos
- Delivered by hospitals
Diagnostic Reference Level
- DRN, Diagnostisk referensnivå
- Recommendations by authorities
There are no dose limits regarding patients,
but irradiation must always be justified and optimized
Effective dose in diagnostic radiology
| Source of exposure | Effective dose |
|---|---|
| Dental X-ray | 0.005 mSv |
| Chest X-ray (single projection) | 0.02 mSv |
| Scull X-ray | 0.06 mSv (*) |
| Mammography | 0.4 mSv |
| Lumbar Spine X-ray | 1 mSv |
| Head CT Scan | 2 mSv |
| Chest CT Scan | 8 mSv |
| Abdomen & Pelvis CT Scan | 15 mSv |
(*) Comparable to exposure during transatlantic flight
Special patient subgroups
X-ray techniques that yield high doses
- Computed tomography
- Angiography & intervention
Of special concern due to inclusion of healthy individuals
- Mammography screening
- Medical research studies
Patient groups that require special attention
- Pediatric patients
- Pregnant women
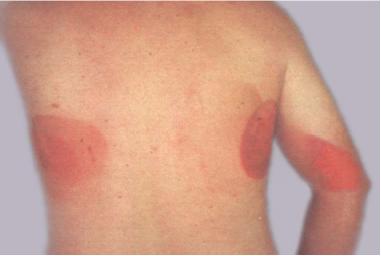
Acute (deterministic) effects - patient
| Effect | Skin dose threshold | Single-dose Onset |
|---|---|---|
| Early transient erythema | 2 Gy | Only hours |
| Temporary hair loss | 3 Gy | ~3 weeks |
Functional loss of irradiated organ or tissue, threshold dose exist, appear after days/weeks
Acute (deterministic) effects - patient
| Effect | Skin dose threshold | Single-dose Onset |
|---|---|---|
| Main erythema | 6 Gy | ~10 days |
| Permanent hair loss | 7 Gy | ~3 weeks |
| Dermal atrophy | 10 Gy | >14 wk (1st phase), >1 yr (2nd) |
| Induration (fibrosis) | 10 Gy | differs |
| Telangiectasia | 10 Gy | > 1 year |
| Late dermal necrosis | >12 (?) Gy | > 1 year |
| Dry desquamation | 14 Gy | ~4 weeks |
| Late erythema | 15 Gy | ~6-10 weeks |
| Moist desquamation | 18 Gy | ~4 weeks |
| Secondary ulceration | 24 Gy | > 6 weeks |
Read more: IAEA Rad Prot in Cardiology
Radiation dose indicators...?
- DAP - Dose-Area Product (Gycm²)
- AK - Air-KERMA (mGy)
- PSD - Peak Skin Dose ≈ AK
- CTDIvol - Volume Computed Tomography Dose Index (mGy)
- DLP - Dose Length Product (mGycm)
Note:
DAP unity prefix can vary between vendors…!
Ex: Gycm² , mGydm², etc…
Alarm levels for angio/intervention
| AK (Air Kerma) | To do |
|---|---|
| 3000 mGy | Inform patient, dose report to medical physicist |
| 10000 mGy | Inform patient, referral to dermatologist |
Note:
2000 mGy is fractional target dose at radiotherapy
Subgroup alarm levels
Interventional cardiac procedures
| Procedure | DAP¹ (3 Gy equivalent) | DAP² (10 Gy equivalent) |
|---|---|---|
| Coronar Angio | 550 Gycm² | 1950 Gycm² |
| PCI | 200 Gycm² | 800 Gycm² |
| Coronar Angio + PCI | 300 Gycm² | 1050 Gycm² |
| TAVI | 250 Gycm² | 900 Gycm² |
1 Inform patient, dose report to medical physicist
2 Inform patient, referral to dermatologist
X-ray tube angle: PA = best!
Exception: neonatal procedure where pat is placed directly on the detector in AP-position
Use zoom function sparsely...
…and if possible:
- Normal dose level (avoid high dose)
- Low pulsed radiation (avoid continous/30 images per sec)
Simple steps to minimimze YOUR dose!


 Sofia Skyttner
Sofia Skyttner
Read more: Geijer et al Eur. Radiol. 12 (2002)
Mammography screening
- Compression (a.k.a. kompression)
- Improved image quality
- Less patient (and staff) dose
Research study including radiation...?



 Flazingo Photos
Flazingo Photos
Strålskyddskommitté- & Etikansökan
Children more radiosensitive


 Sofia Skyttner
Sofia Skyttner
Läs mer: ICRP Publication 60
Guidelines in pediatric X-ray
Dedicated equipment that allow for
- High kV-short exposure time techniques
- Easy grid (raster) removal
- Flexible AEC (chamber selection)
Special care
- Consider additional beam filtration
- Avoid antiscatter grids for the smallest children, or use low ratio grids (8:1)
- Use low dose detectors (i.e. high DQE digital detectors)
- Use low dose fluoro (possibly replace conv X-ray)
- Use TCM in CT and/or scan protocols adjusted to age/size
- Use gonad shield for boys, not for girls & neonatal patients
Foetus - extra radiosensitive
Especially during first trimester!



 Image Editor
Image Editor
Read more: ICRP Report 84
Pregnant patients...?
Female patients in fertile age shall always be
asked for pregnancy before X-ray!
- Female pat in fertile age, vomiting for 10 days
- Gastroscopy without remark, day 1
- Rad ask for CT-abdomen, day 2
- Radiographer do the exam
- Exam shows nothing remarkable
- Finally physician asks for pregnancy test, pat pregnant…!
1) Unjustified radiation of patient (and fetus)
2) Pregnancy question failed (three times…!)
X-ray of pregnant patient...?
X-ray department shall inform medical physicists about the examination if…
- …fetus was either in or partly in radiation field
- …fetus was not the patient
Termination of pregnancy...?
Generally fetus dose is: < 0.1 mSv @ conv X-ray & < 10 mSv @ CT exams
Early/mid pregnancy
Fetal dose < 100 mSv: Termination of pregnancy NOT justified based upon radiation risk
Fetal dose 100-1000 mSv: Magnitude and type of fetal damage depend on dose and stage of pregnancy, physician decision should be based upon individual circumstances
Late pregnancy
Fetal dose < 1000 mSv: Not likely to result in malformations or birth defects
Read more: ICRP 89
Coffee break!
At the hospital of Fairy Town...
- New HOMEMADE sign at the MR dep
- “Välkommen till Magnetröntgen”
- What do YOU say…?
Medical Imaging
Ionizing Radiation
- Interventional radiology
- Diagnostic radiology
- Nuclear Medicine
- Radiation treatment
Non-Ionizing Radiation
- MR
- Ultrasound
Itchy feeling when working with X-rays
- Probably extra radiosensitive, avoid working with X-rays
- Please, use double aprons (strålskyddsförkläde)
- Not possible to perceive ionizing radiation
Distance, time & shielding!
New hybrid X-ray equipment
Remember mobile shields...!
- Physician and nurse at intensive care patient
- Patient beds close to each other
- Radiographer takes X-ray without shields…!
Unjustified irradiation of staff and adjacent pat
Shields at mobile X-ray systems
Exception: neonatal examinations
First come, first served...?
Först till kvarn får först mala…?
- Lead aprons for everybody?
- Mobile shields…?
- Not enough lead glasses…!
Adequate lead apron...?
- No cracks…?
- Lead equivalence (0.25/0.35/0.50 mm)…?
- Covering…?



 Ted Eytan
Ted Eytan
Is the room empty...?
- Anesthesia nurse prepares anesthetic equip
- Radiographer no 1 prepares pat for CT
- Radiografpher no 2 starts CT exam
Unjustified irradiation of staff, anesthesia nurse in room during CT overview image
CT scan protocol correct...?
- Radiographer 1 forgets delay (50s) before CT exam
- Radiographer 2 next to patient for IV injection
- R 1 exposed without apron, but with dosimeter
Unnecessary irradiation of staff
Pregnant staff...?
- Contact your medical physicist
- Personal (monthly) dosimeter
- Always right to avoid working with ionizing radiation
Avoid working close to patient at:
- Angiography/interventional systems
- Computed tomography systems
- C-arms (large body)
Scattered radiation at C-arm


 Dennisthemonkeychild (left), Sofia Skyttner (right)
Dennisthemonkeychild (left), Sofia Skyttner (right)
Read more: ICRP Report 85
Scattered radiation at CT
Pregnant staff at MR...?
Back to Fairy town hospital...
- X-ray grid (raster) breakes in afternoon
- Engineer says delivery tomororrow
- Radiographers are informed…
- …but during night shift: grid is re-used…!
X-rays of three pat until radiologist complains about image quality…!
X-ray licence necessary
- Surgeon wants to save C-arm images
- Presses left foot pedal
- Left foot pedal = high dose
Unjustified irradiation of pat, education necessary
X-ray licence part II
- Radiographer wants to CT scan additional 2 cm
- Pushes the button “one more”
- Med phys discover CT exam with 41 helical series
Unjustified irradiation of pat,
each keystroke = 0.5 mm scan with 20 mm collimation…!
Fat inside or outside peritoneum (a.k.a. bukhinnan)...?
Radiation shield…!
Mr BodyBuilder 2016...!?
Physically fit patient = malnourished patient…?



 Judge Vag
Judge Vag
Extremely tall or short patient...?
Collimation at CT...?
Less patient (and staff) dose!


 Sofia Skyttner
Sofia Skyttner
i.e. adjusting scan lenght
Collimation at conventional X-ray...?
Improved image quality & less patient (and staff) dose!


 Yale Rosen
Yale Rosen
i.e. adjusting X-ray beam length and width (inbländning)
Patient with stiff neck...?
Patient too low in gantry opening...?
- Worsening image quality (photon starvation artifact)
- Increased dose to skin-deep frontal organs
Arms down...? Hands up!



 … (left), hajime yoneya (right)
… (left), hajime yoneya (right)
Worse image quality (patient out of field artifact)
Unruly patient...? Fixate!
Shadows and streaks (movement artifacts)
Jewelry in scanning area..?
- Pat with cervical spine collar hiding necklace and earrings
- Pat has zippers in sweatshirt, and carries errings
Citation
“Pat face and ears are full of piercing…!”
Patient with dental filling/hip implant...?



 NIH (left), Radiopedia (right)
NIH (left), Radiopedia (right)
Dark and light streaks, increased noise (metal artifacts)
Tattooed patient...?
Vendor QA of the CT...?
- Radiographer finds dose levels high
- R contacts medphys
- Vendor has changed CT protocols…!
Unnecessary irradiation of pat during couple of days
Physicist measurements...?
- Medphys tests the AEC of a CT system
- Medphys forgets to restore the CT afterwards
- Nobody notices this…
- …but medphys when returning a couple of weeks later
Unnecessary irradiation of about 100 pat
Carousel of communication...?
- Radiographer asks for pat to drink 1.5 l water
- Emergency nurse forgets to tell intensive care nurse
- Intensive care nurse forgets to ask radiographer
Not optimized examination of pat, X-ray taken with bad image quality
Right patient...?
- Ward nurse delivers pat for CT exam
- Chatty staff, “messy”, only forename
- “Is this Amelie?”, “Yes, this is Anneli”
- CT -/+ ivk exam started, already contrast in kidneys…!
Unjustified irradiation of pat
Right name! Right ID no...?
- Ward delivers pat for CT exam
- Radiographer asks “Is this Frans?”
- Ward nurse + pat answ “Yes”
- Radiographer asks for ID no, pat answ with birth year
Unjustified irradiation of pat.
Physician noticed wrong pat being examined.
Pat "ordered" och "delivered"!
- Radiographer calls for supplementary X-ray
- Transport service pick up pat from ward
- Transport deliver pat with one word “supplementary”
- Radiographer takes X-ray without asking for name and ID no
Unjustified irradiation of pat that had took over ward room, ID bracelet necessary!
Right ID bracelet! Right patient...?
- Pat from emergency room to X-ray room
- Radiographer scans ID bracelet without asking for name & ID no
- Radiographer takes one X-ray, pat protests: not left hand, right…!
Unnecessary irradiation of pat, pat has wrong ID bracelet
Radiation related accidents/unintentional exposures
Electronic management!
Check box: Radiation related accident
Check box: X-ray
Avoid blaiming the messanger!
- Radiographer's dosimeter shows increased staff dose
- Chech routine: radiographer always behind shield
- Medphys measures lead equivalence: ordinary glass…!
- Cleaning staff asked her husband for help regarding glass breakage…!
Unjustified irradiation of staff









.jpg/512px-Coffee_break_(3457656569).jpg)


.jpg/1200px-Blood_test_(1).jpg)













_main_lecture_hall_1972.jpg/1200px-École_de_Physique_des_Houches_(Les_Houches_Physics_School)_main_lecture_hall_1972.jpg)





