Firearm Suicide: The Hidden Side of Gun Violence
Jim Scotland
April 24, 2018
Overview
- Shed light on hidden issue of firearm suicide
- Frame issue relative to homicide deaths and overall suicide
- Explore potential impact of region, laws and ownership rates
- Develop regression model to predict gun suicides
- Use machine learning to assess critical gun law interventions
The Problem
- The individual most likely to kill a gun owner is himself
- Suicides made up 60% of gun deaths in 2016
- Almost 23,000 firearm suicides in 2016 and trend is rising
- In 44 states, rate of gun suicide exceeds gun homicide
- The greatest risk to a gun owner is their own gun
Best States for Gun Owners?
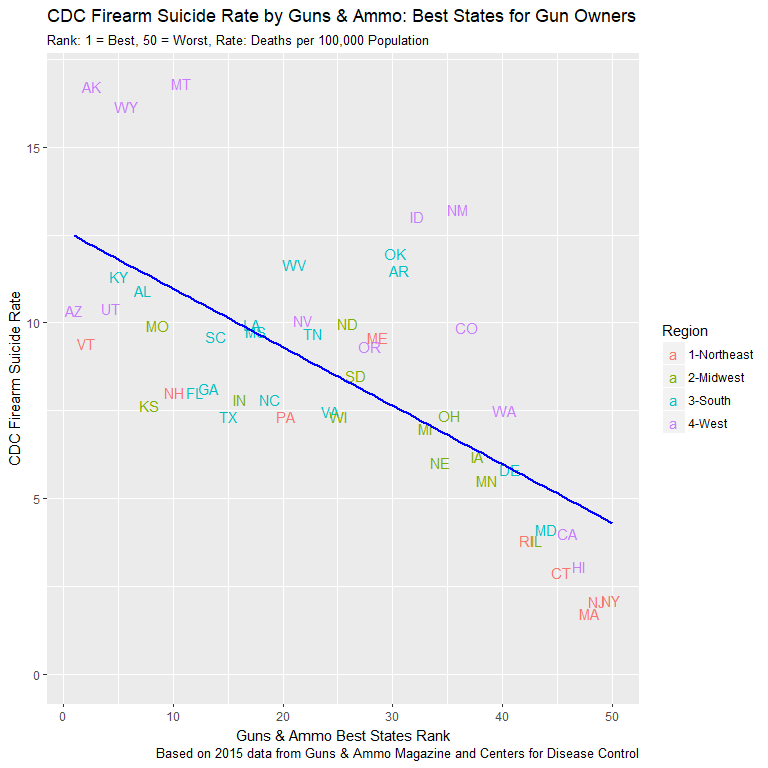
- Guns & Ammo state rankings find curious correlation
- MT ranked 11th by G&A, 1st in gun suicides
- MA ranked 48th by G&A, 50th in gun suicides
- What exactly does “Best for Gun Owners” mean?
Firearm Suicide as Target of Study
- Firearm suicide takes more lives than homicide
- Vast majority of states face far higher firearm suicide rates
- Suicide is more critical problem in rural states
- Suicide methods and trends vary across regions
- Within regions, gun suicides drive higher rates in rural states
Suicide Takes More Lives, Getting Worse
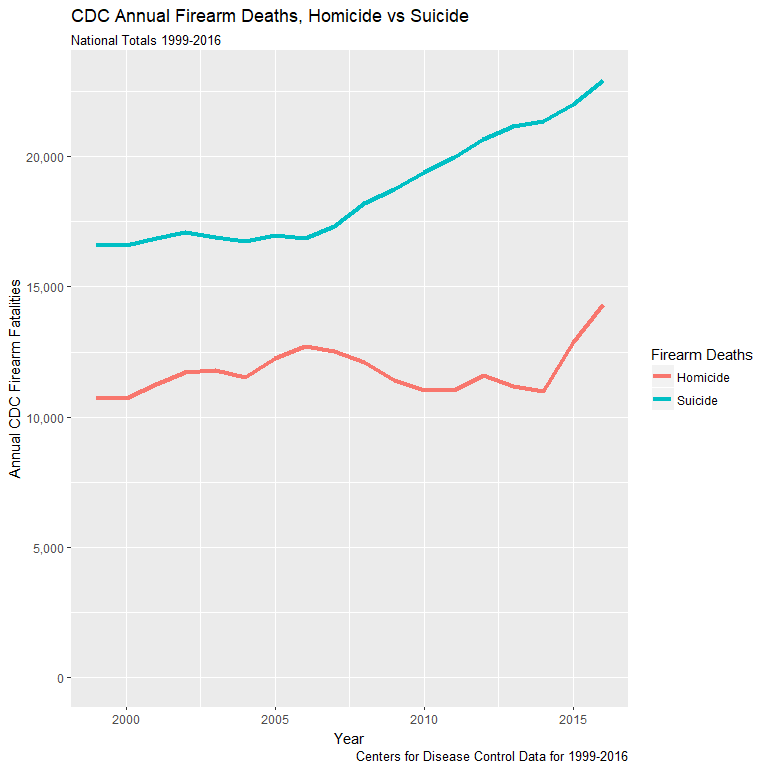
- Firearm suicides historically outpace homicides
- Sharp and steady rise in suicides since 2008
- Firearm homicides more stable but spiking recently
Firearm Suicide Minus Firearm Homicide
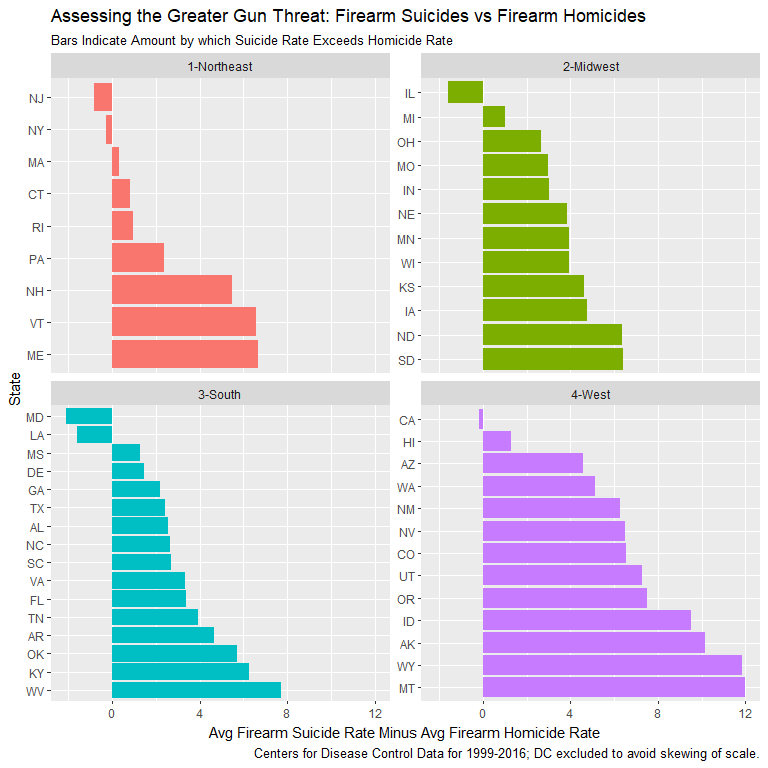
- Firearm suicide rate 2X homicide rate on average
- Disparity greater in rural states
- Only six states w/ higher homicide rate
Suicide Rates Higher in Rural States
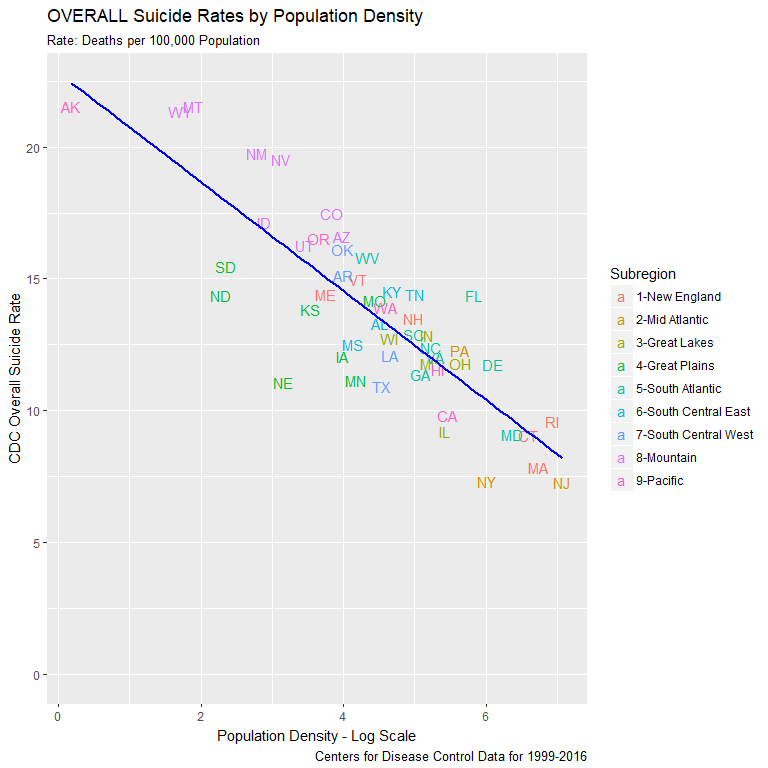
- Sparsely populated states face higher suicides
- Mountain states experience most extreme levels
- Similar Plains states all well below Mountain rates
- Northeast posts lowest suicide rates
Regional Variations in Suicide Modality
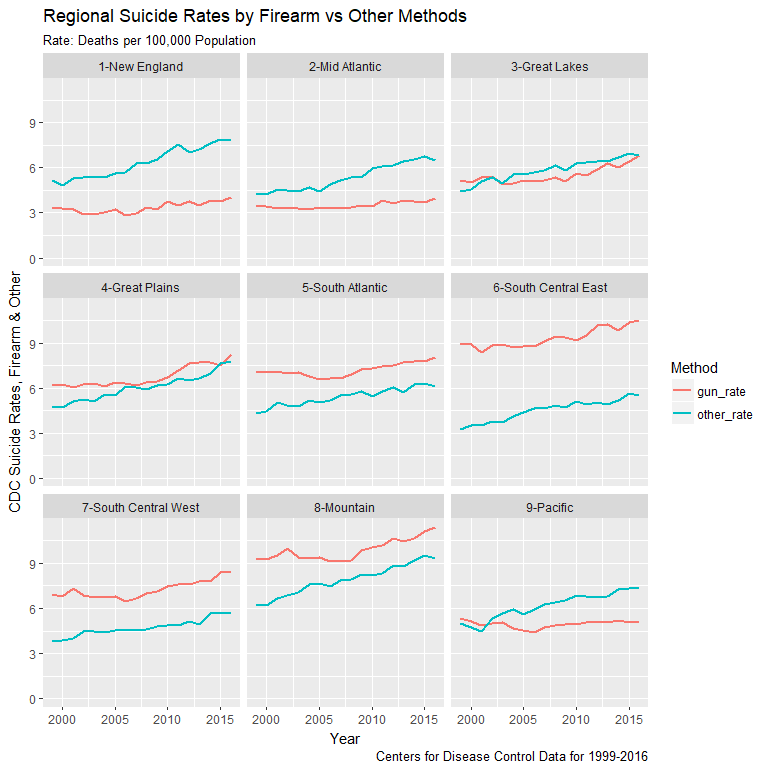
- Firearm suicide rate (FSR) lower and trendline flatter in Northeast and Pacific
- FSR sharply higher and rising in South and Mountain regions
Rural vs Urban Divide within Regions
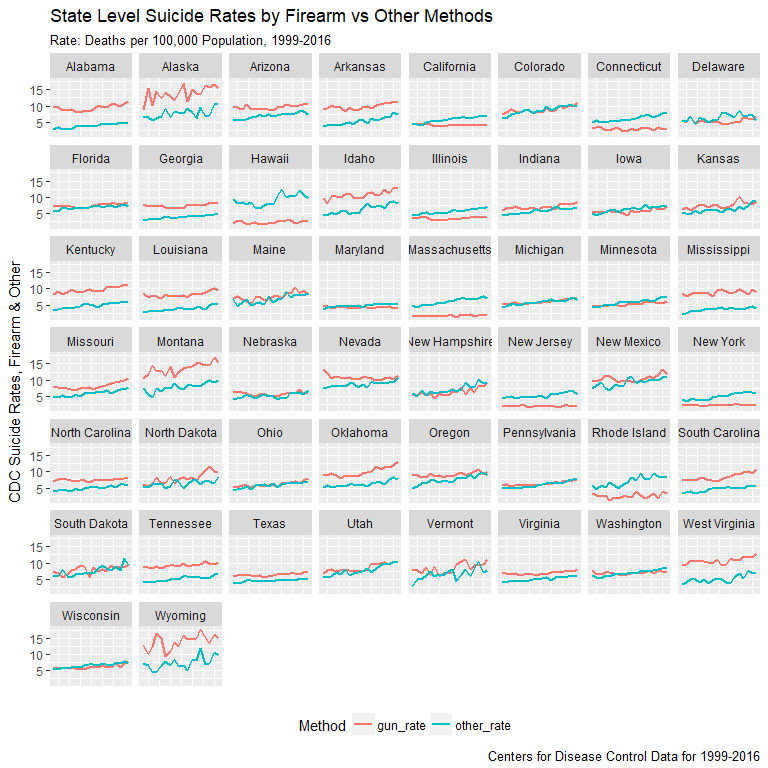
Examples of Regional Divide
- Massachusetts vs Maine
- New York vs Pensylvania
- Illinois vs Indiana
- Texas vs Oklahoma
- California vs Oregon
Guns Drive Above Average Suicide Rates
- Since 1999, guns accounted for 58% of deaths in states with above average suicides
- They account for 48% of deaths in below average states
- In three lowest suicide rate states, guns account for 22%-32% of deaths
- In three highest rate states, guns are used in 63%-65% of suicides
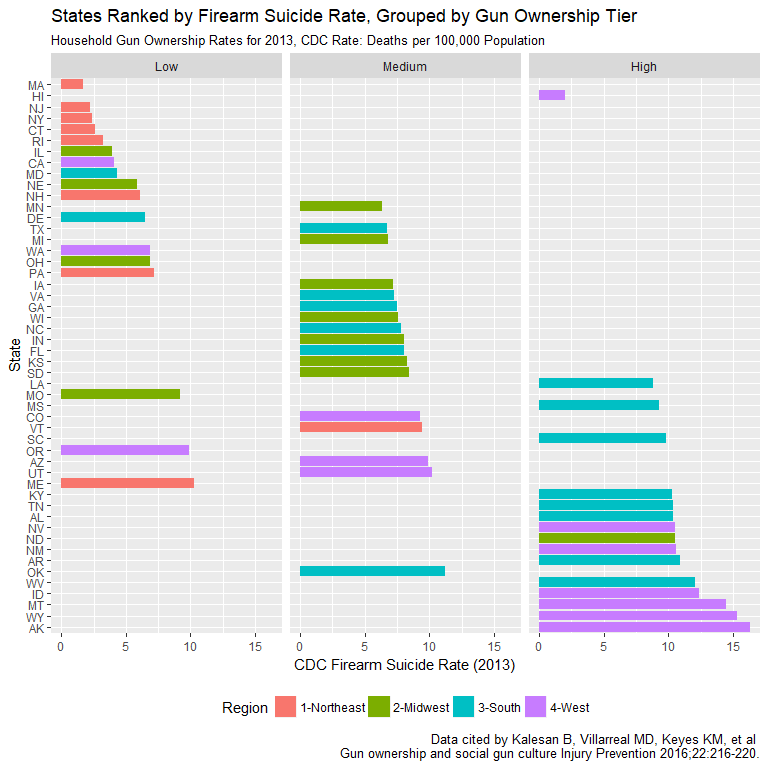
Gun Ownership and Firearm Suicides
- Gun ownership data from 2013 Kalesan survey
- Strong relation between higher gun ownership and higher suicide rates
- Regional and rural/urban variations are evident
- Ownership data for one year only limits analysis
More Guns, More Gun Suicides
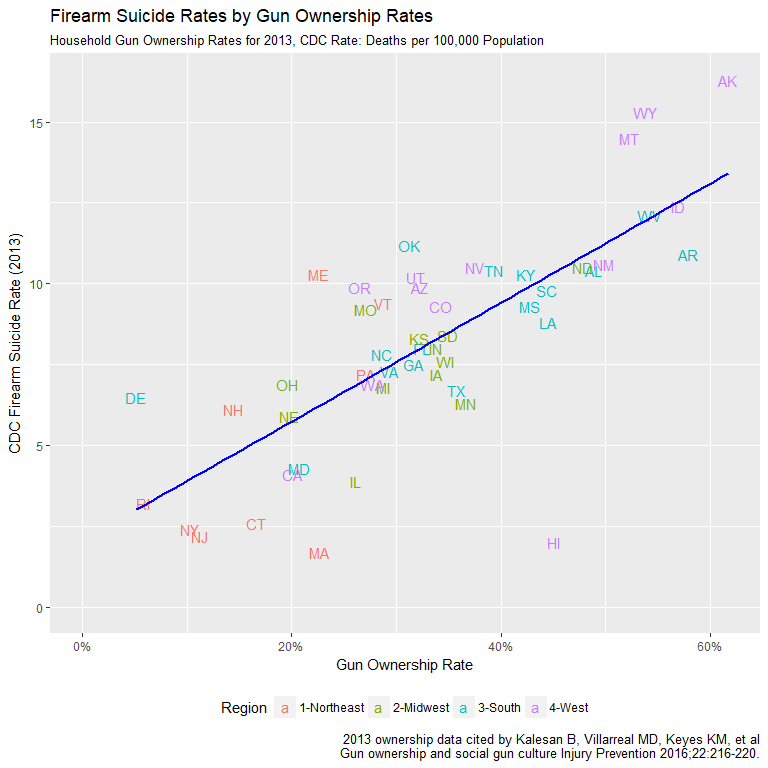
- Ownership rates strongly correlated with FSR
- Correlation of 0.748 and r-squared of 0.559
- Divide between rural and urban apparent again
Mapping Gun Ownership and FSR Levels
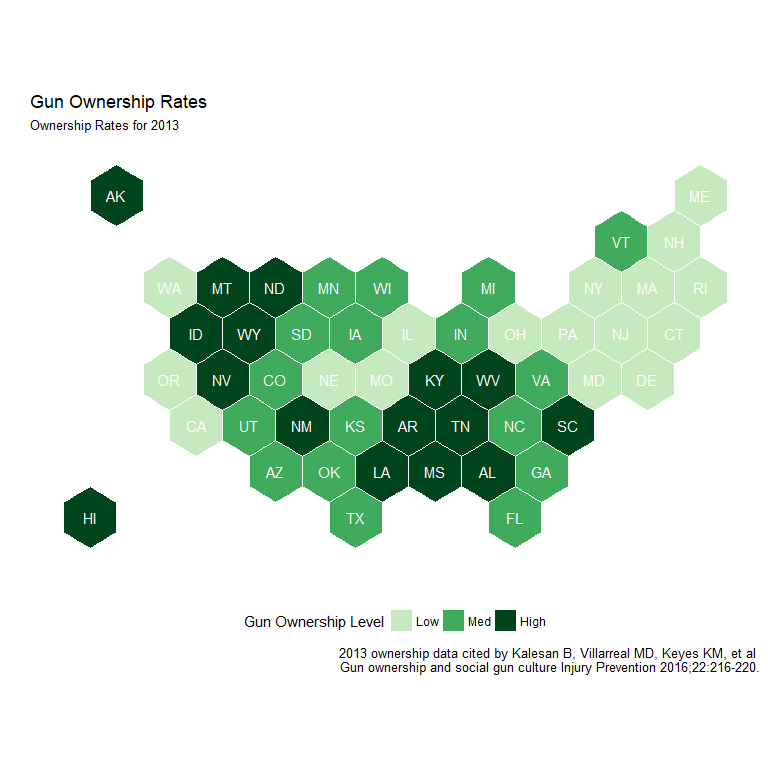
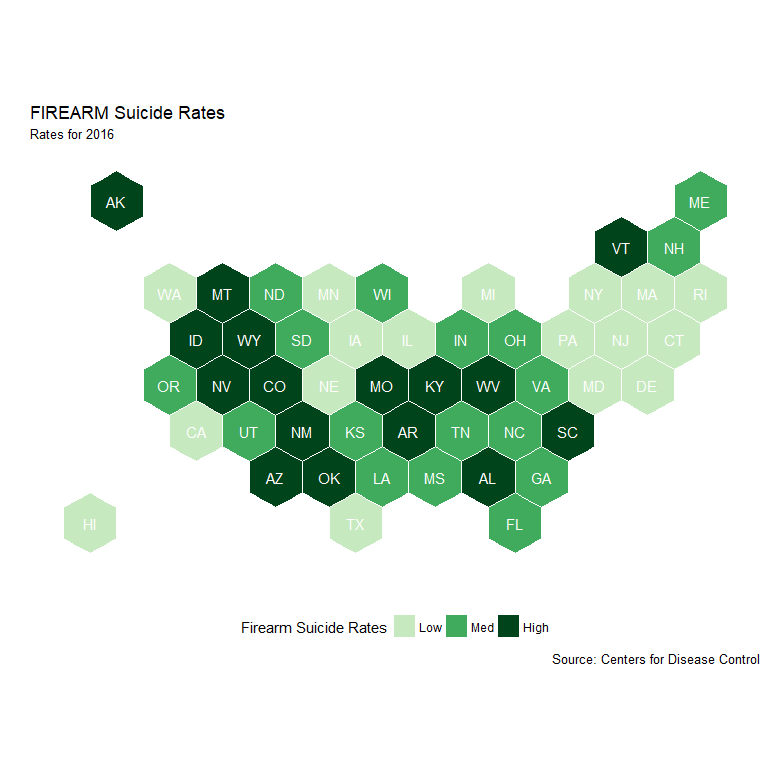
Ownership Tier and Firearm Suicide Rates
- High ownership tier has 12 of 13 highest FSR states
- Low ownership tier has 11 0f 13 lowest rates
- Hawaii data likely incorrect (see full report)
Giffords Gun Law Grades
- Giffords Law Center Data for 2014-2016
- Ratings show relation between weak laws and gun deaths
- Rankings also display relation with firearm suicide rates
- Data limited to three years impacting deeper exploration
Giffords Grades and Gun Deaths
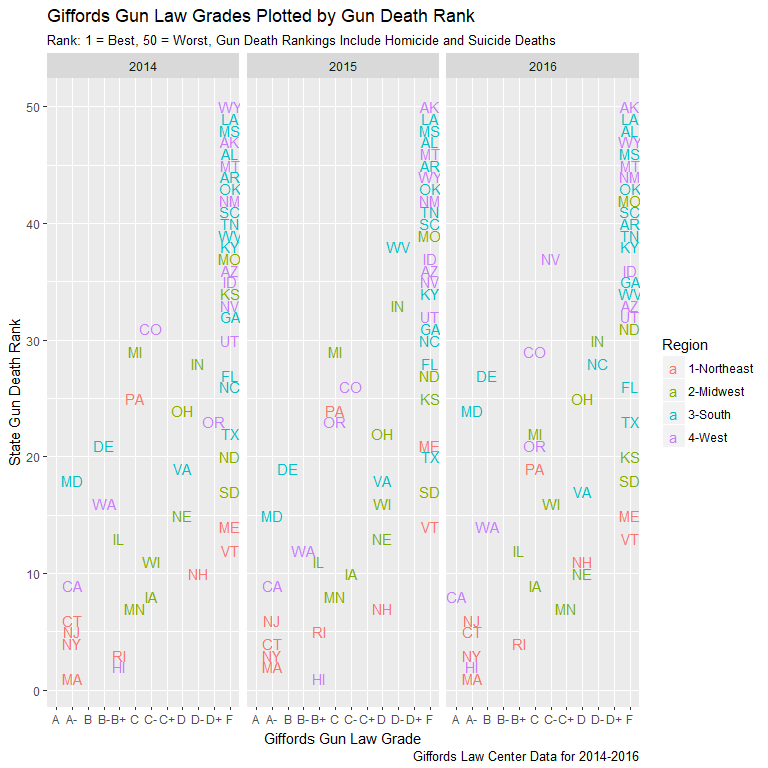
- Half of states receive gun law grade of “F”
- Worst gun death ranks dominated by “F” states
- States with A-B grades boast lowest gun deaths
- Similar relationship for firearm suicides
Mapping Giffords Grades and FSR Levels
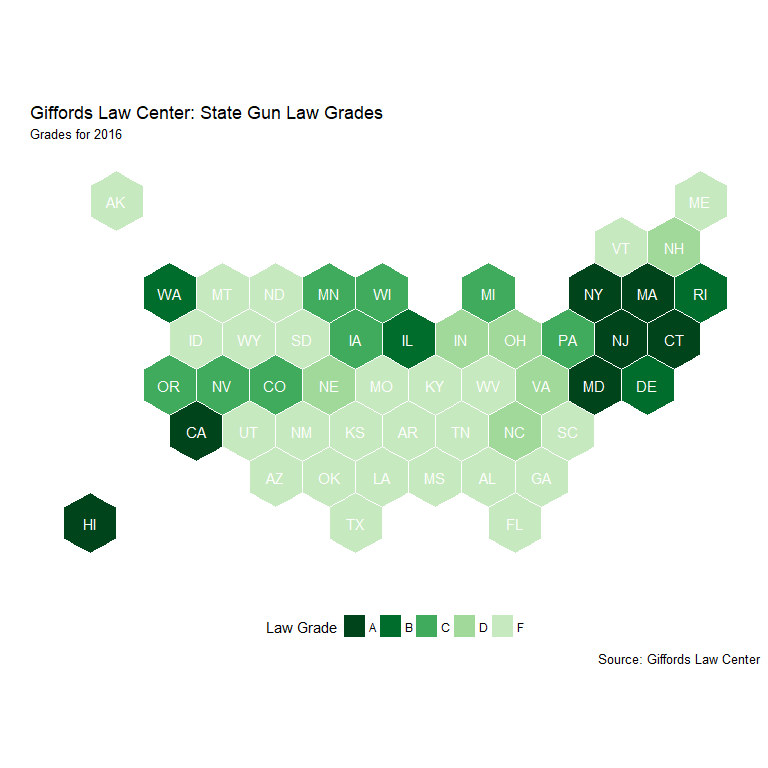

F-Grade and Overall Suicide Rates
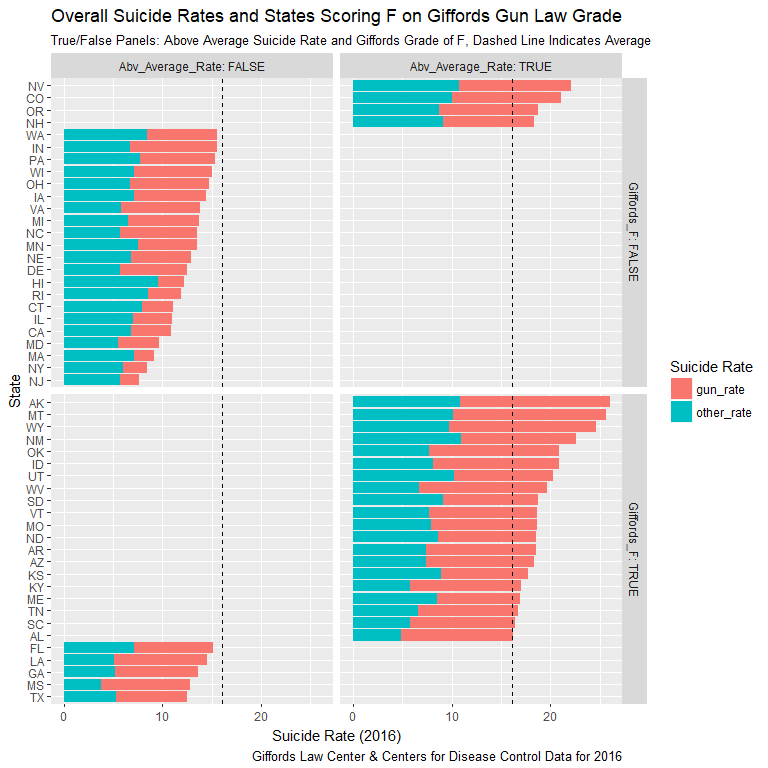
- 41 Above/Below Average rankings indicated by Giffords “F”
- 21 “Non-F” states below average
- 20 “F” states above average
- Clear prevalence of gun suicides in above average states
Strong Laws, Fewer Firearm Suicides
- Gun regulation varies widely by state and region
- Increased regulation largely limited to coastal states
- Strong relation between regulation and firearm suicides
- Reduced gun laws, increased FSR deaths
Gun Regulation Varies by State & Region
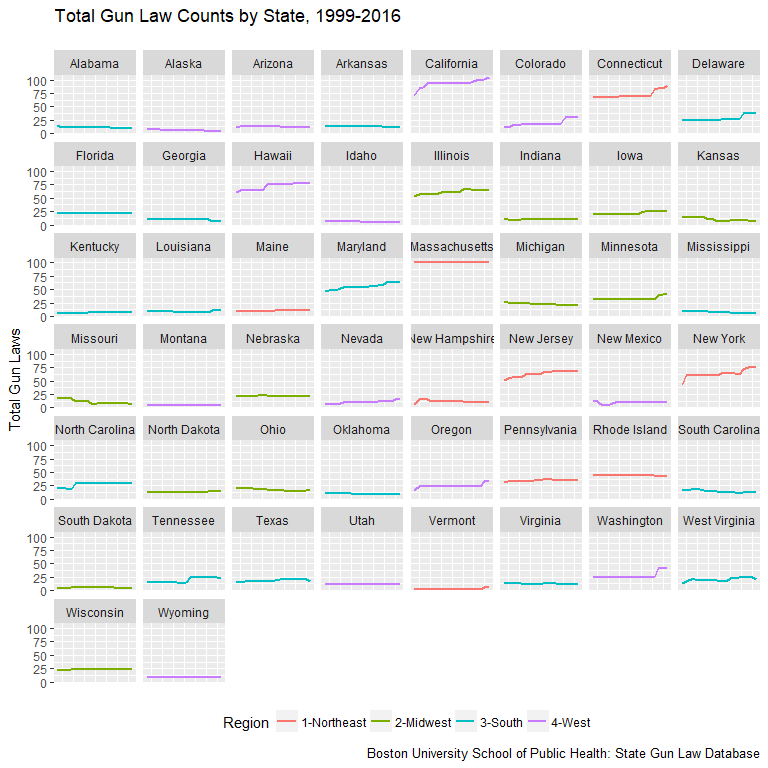
- Number of laws and trends wildly disparate
- Variation mirrors rural-urban divide within regions
- Northeast has strongest gun laws nationally
- Maine & Vermont laws closer to South or Mountain West
Increased Regulation on Coasts
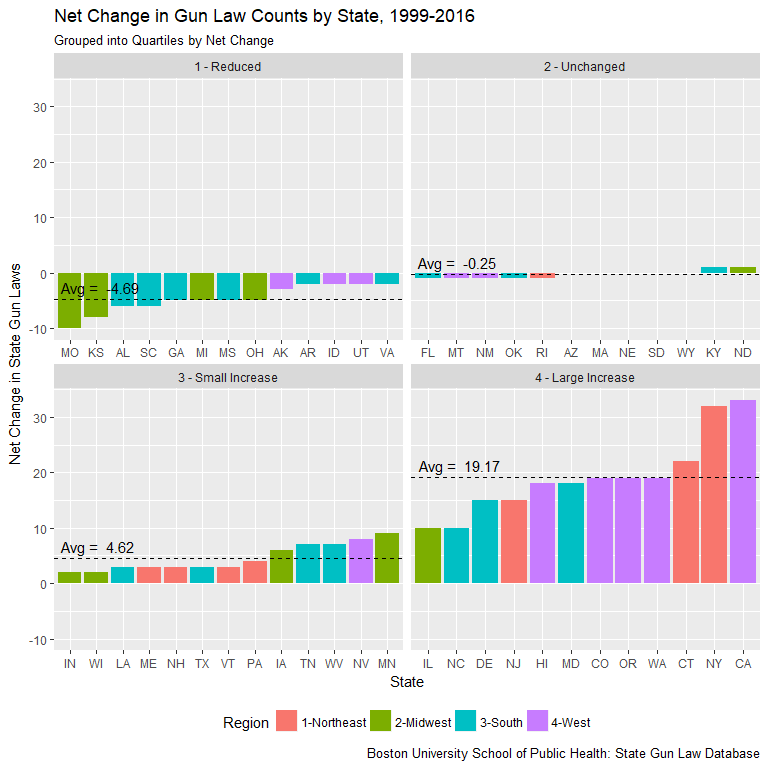
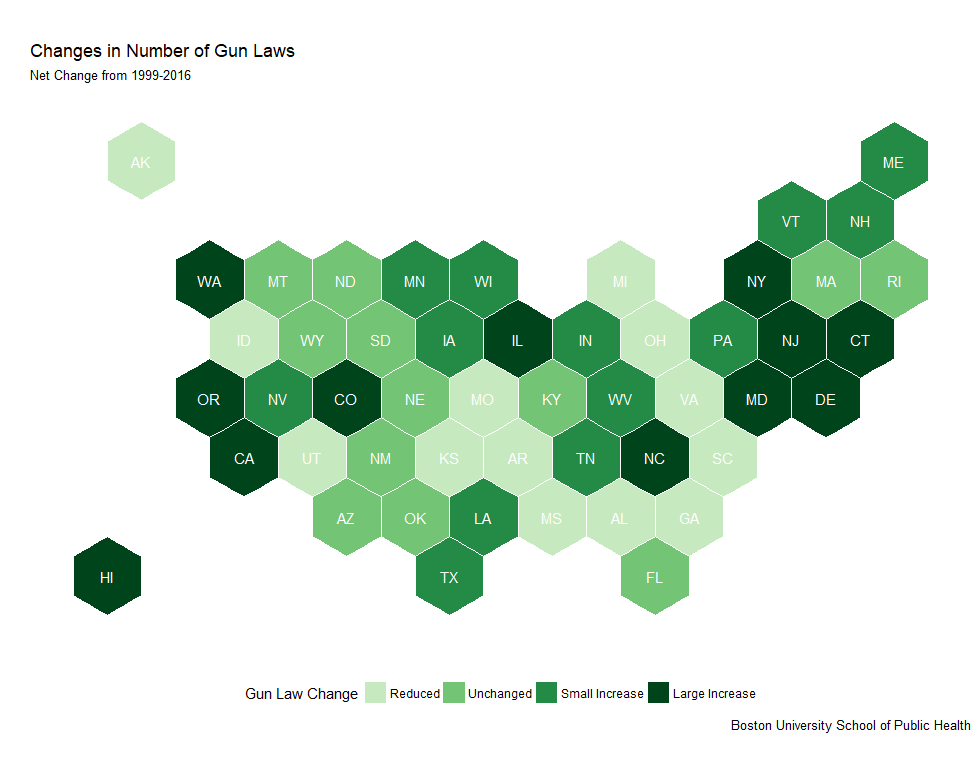
Gun Law Changes 1999-2016
- Significantly increased regulation (10+ laws) in only 12 states
- Increases concentrated on East and West coasts
- Laws decreased in 18 states across South, Midwest and West
Laws Strong Indicator of FSR Level
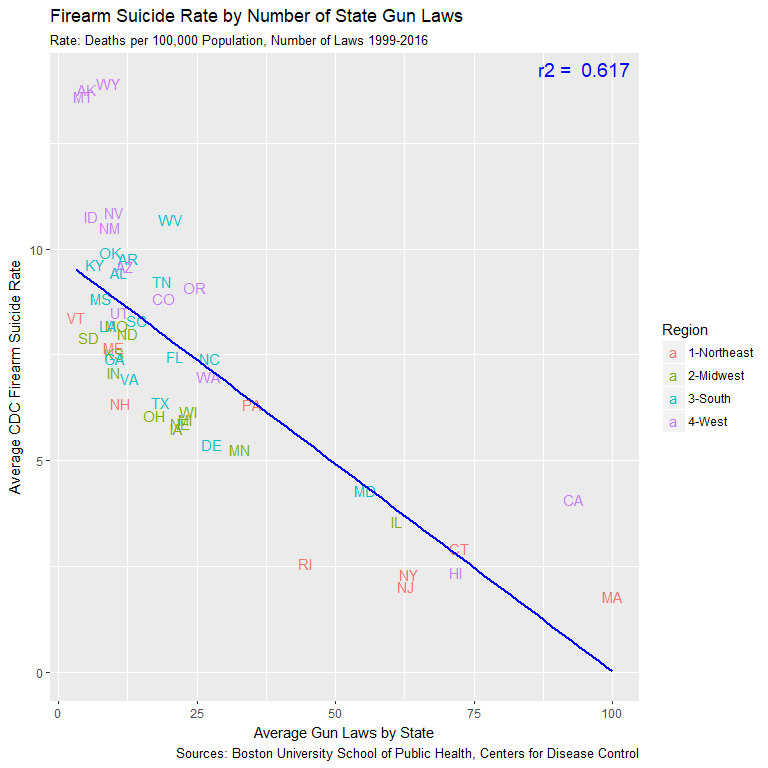
- Number of laws explains 61.7% of variation in state FSR levels
- High regulation coastal states have far lower FSRs
- Western states dominate the low regulation, high FSR corner
- Plot presents reversed mirror image of earlier ownership plot
Relationship Stronger at Regional Level
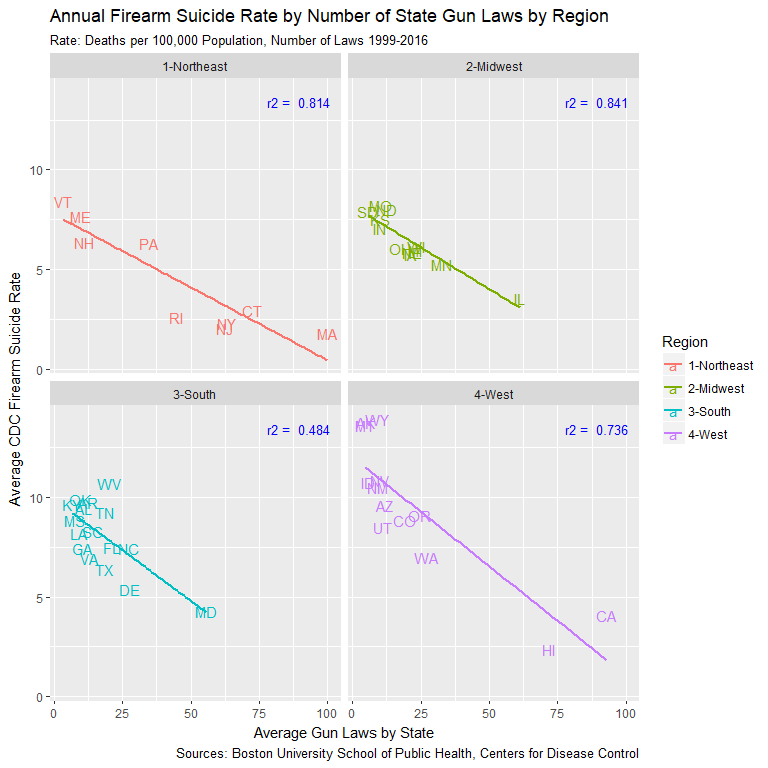
- Regional plots call out rural vs urban divde once more
- R-squared values markedly higher by region
- AK, WY, MT remain unfortunate outliers at top of FSR range
Reduced Gun Laws, Increased FSR Deaths
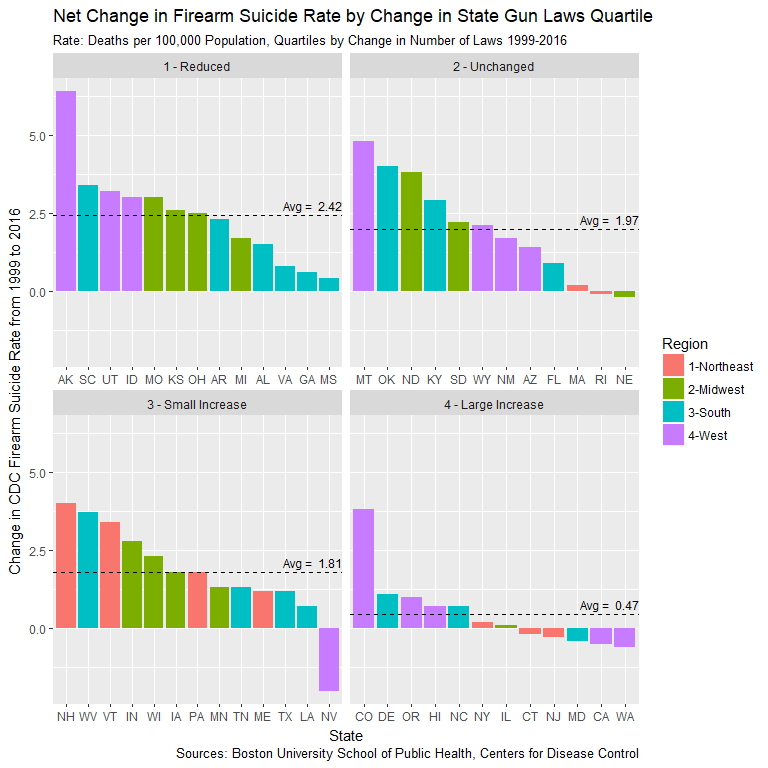
- Reduced gun law states averaged 2.42 increase in FSR
- Large increase states (10+ laws) saw only 0.47 increase
- 5X difference in FSR change between two groups
- Changes occur amid rise in national suicide rates
Mapping Law Change to FSR Change
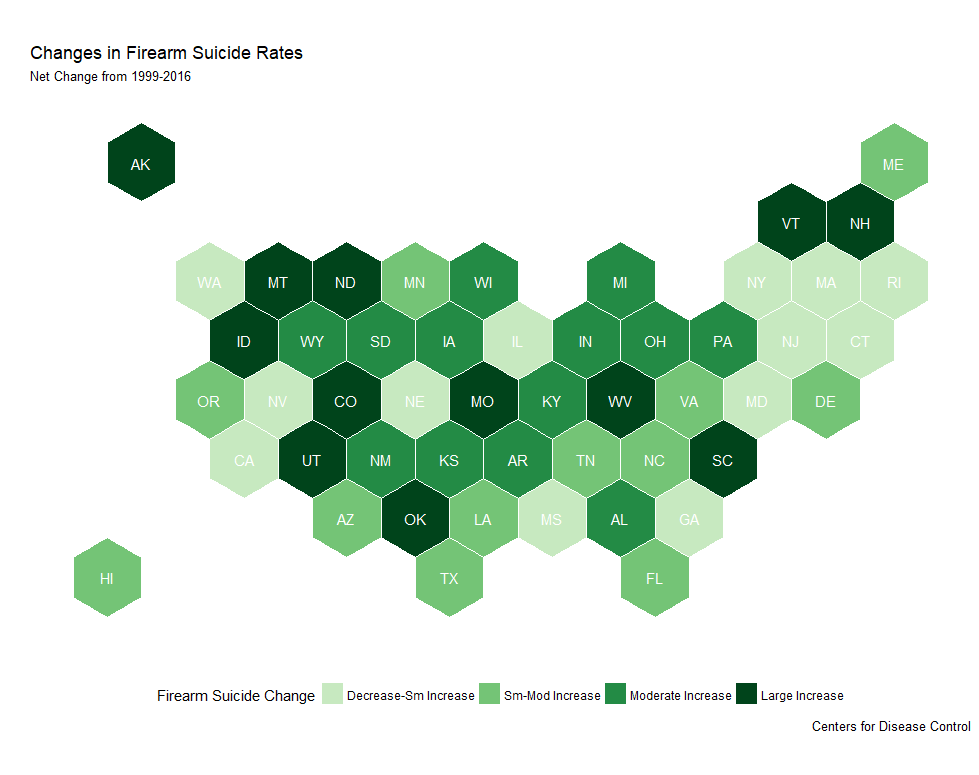
Select State Comparisons
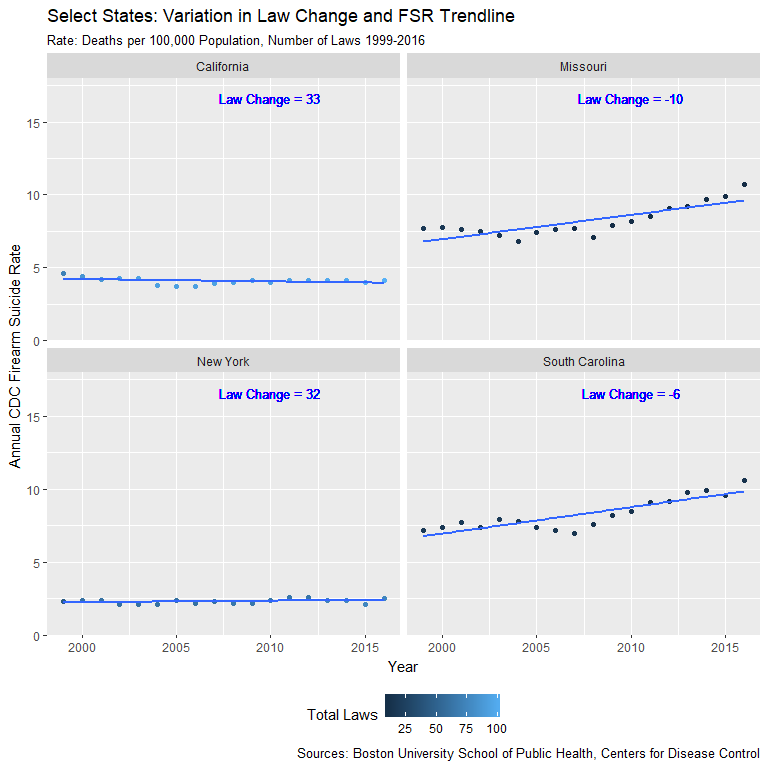
- California +33 gun laws, FSR fell 0.5/100K
- Missouri -10 gun laws, FSR rose by 3.0/100K
- Estimated 176 more Missouri suicides in 2016
- Estimated 183 lives saved in California
- NY: 39 saved lives, SC: 151 more deaths
Regression Model to Predict State FSR
VARIABLES OF INTEREST
- Gun Ownership Rate
- Firearm Laws
- Region
- Population Density
POTENTIAL ISSUES
- Colinearity between variables
- Only one year of ownership rates
- Rising suicide rate
Training Data - 2013 Data Only
- Ownership rate, buyer regulation laws and region West most effective variables
- Ownership rate has greatest impact on model performance but high error range
- Buyer regulations law category more conservative choice over total laws
- Population density strong predictor in isolation, not in combination
- Region = West outperformed all other regional variable options
- Model predicted 82.5% of variation in FSR on the 2013 training data
Model Performance on Test Data
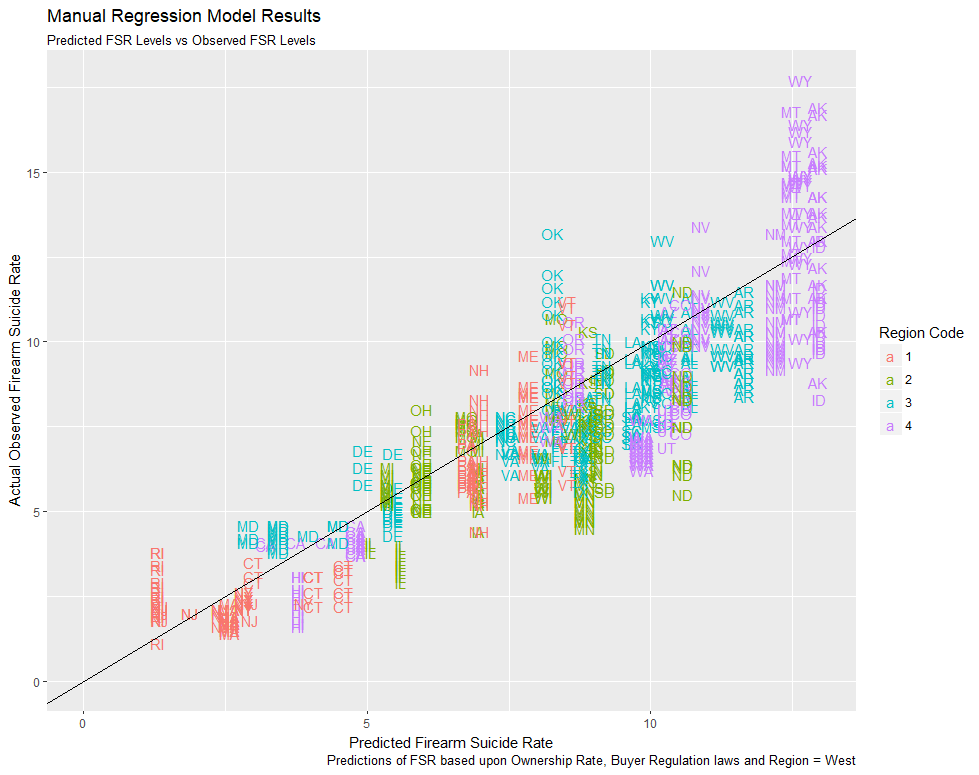
- Model accounted for 77.3% of FSR variation in test data
- RMSE of 1.68 improved on train data performance
- Significant size difference in datasets likely cause of shifts
- Variation at high end of FSR range difficult to predict
Random Forest: Law Categories Only
- Random Forest machine learning technique for higher accuracy
- Inability to see how model achieves improved performance
- Run to explore possibility of using only law variables
- Higher risk of overfitting model to training data
- Train with 70% of data, test on 30%
Random Forest Model Performance
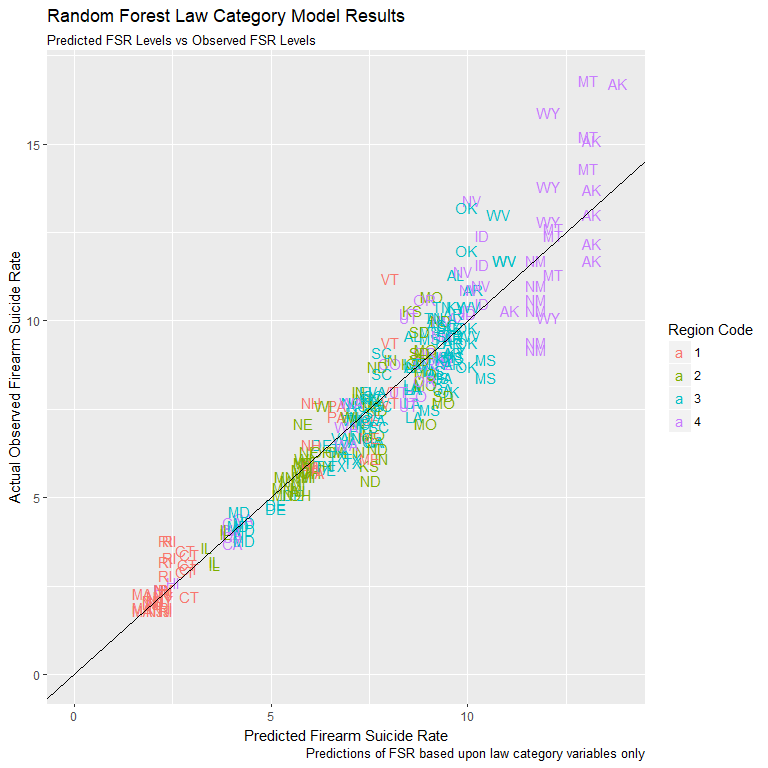
- Random Forest model outperformed manual regression
- Used only 14 law category variables
- Accounted for 90.4% of FSR variation
- RMSE of only 0.945
Gradient Boost Model: All Law Variables
- Gradient Boost machine learning technique similar to Random Forest
- Allows one to glimpse variable impact
- Apply using 132 individual law variables
- Assess law variables most likely to effect FSR levels
- Repeat 70/30 training vs test data split
Gradient Boost Model Performance
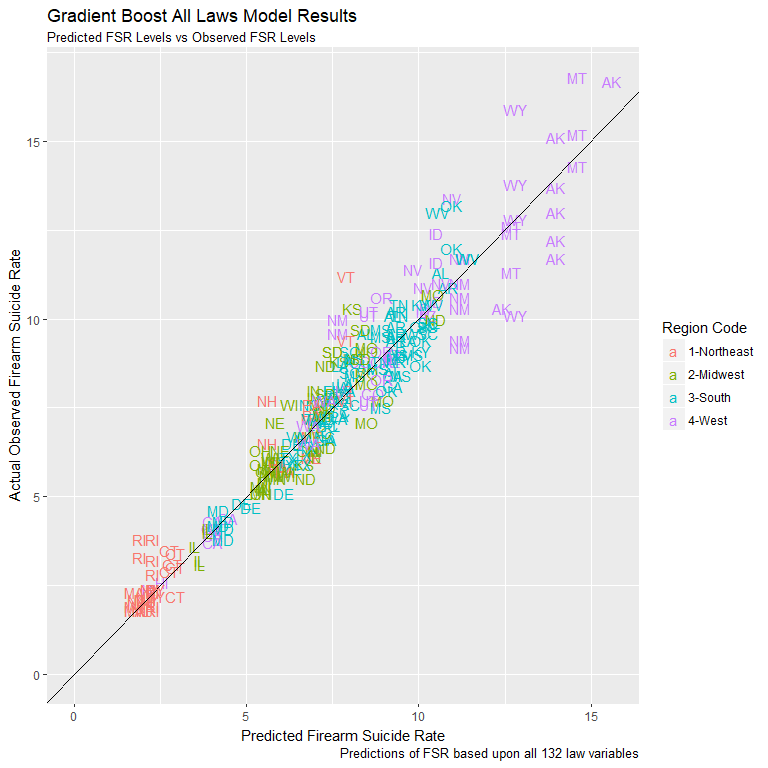
- Outperformed Random Forest law category model
- Accounted for 92.3% of variation in FSR
- RMSE even lower at 0.85
Critical Variables in Model
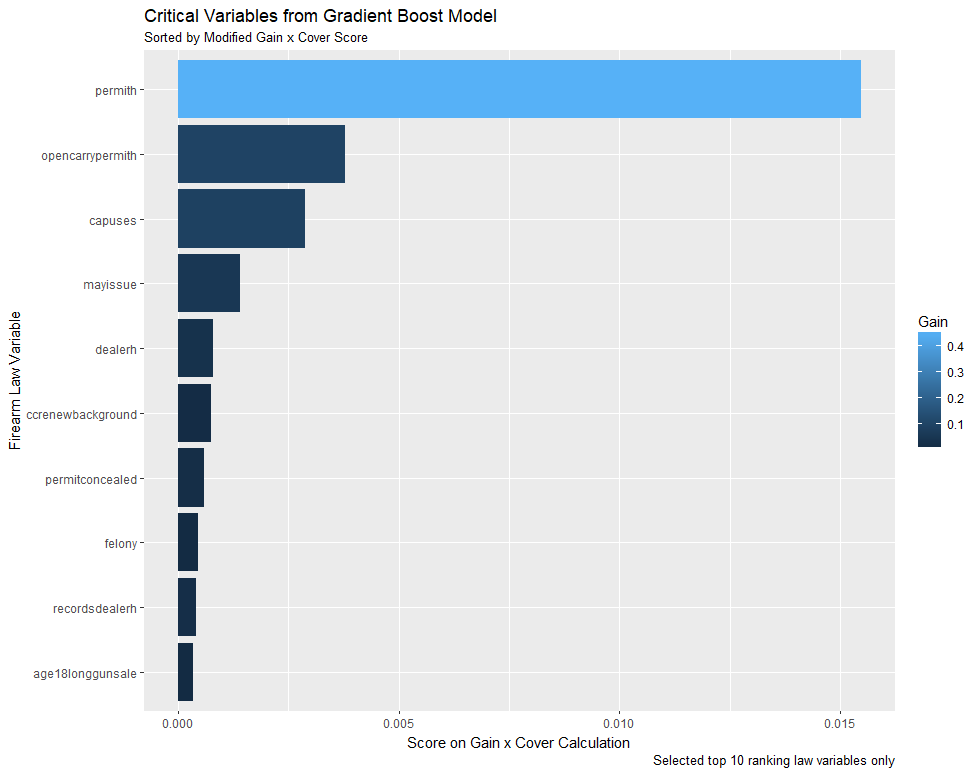
- Plot displays critical variables ranked by gain x cover
- Gain indicates improvement in model accuracy
- Cover indicates number of branches effected
- permith clearly stands out in ranking
- permith: A license or permit is required to purchase handguns
Manual Regression Using Critical Laws
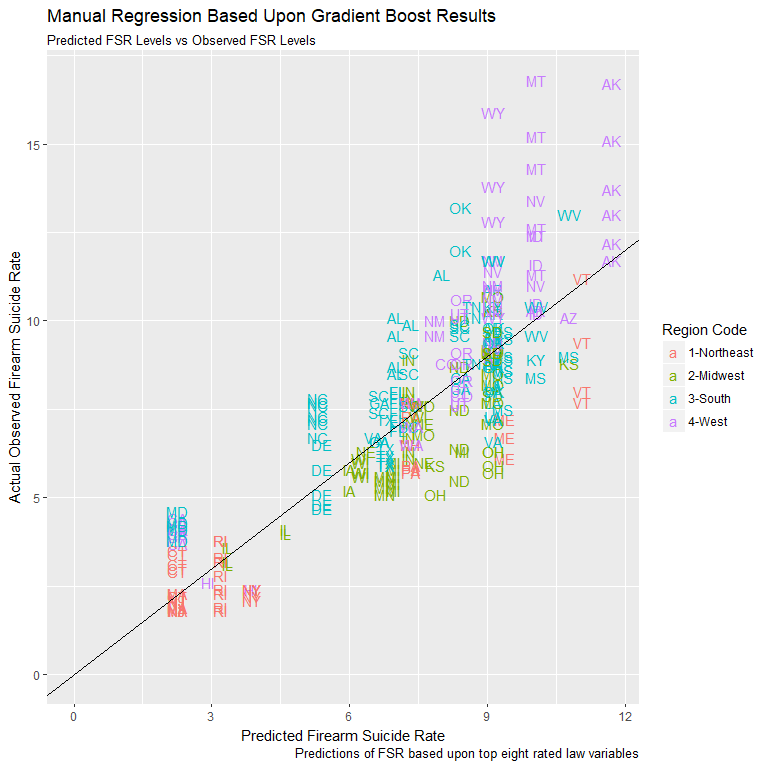
- Built manual regression model using critical law variables
- Dropped two during model build for lack of impact
- Model accounts for 70.9% of FSR variation using 8 laws only
- Less accurate than initial manual regression but respectable
Critical Law Variables Defined
- permith: A license or permit is required to purchase handguns
- opencarrypermith: No open carry of handguns is allowed in public places unless the person has a concealed carry or handgun carry permit
- capuses: Criminal liability for negligent storage of guns if child uses or carries the gun
- mayissue: “May issue” state (granting of cc permits at discretion of local authorities)
- dealerh: State dealer license required for handgun sales
- ccrenewbackground: Concealed carry permit renewal requires a new background check
- permitconcealed: Permit required to carry concealed weapons
- recordsdealerh: Record keeping and retention required for licensed dealers for handgun sales
Conclusions
- Gun legislation makes a difference
- Highly regulated states have guns but fewer gun suicides
- Pursue laws most likely to effect the suicide problem
- Rural states are at greatest risk for firearm suicides
- Self-protection argument is illusory
- Deeper modeling research of law impact would be valuable
Data Sources
- Suicide and homicide rates from Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- Gun ownership data from Kalesan Injury Prevention article
- Giffords Law Grades and Rankings from Giffords Law Center
- State Firearm Law data from Boston University School of Public Health
- Guns & Ammo Best States for Gun Owners
- Complete research paper available here, source code and data available here