library(tidyverse)
getwd()
setwd('your/preferred/working/directory')
donor <- read.csv('https://goo.gl/tm9JQ5')
police <- read.csv('https://goo.gl/T42fHz')
January 17, 2017
Let’s begin by reading the campaign donation and the police incident datasets
Select, create, and rename variables
Select, create, and rename variables
select()keeps the named variables from the dataset- You can also remove variables from the dataset with
- - Nest functions within
select()usually do not work- Exception:
everything()
- Exception:
- Use
'``'for multi-word variables and variable names that begin with numbers
donor %>% select(id, amount, type, party, receipt_date) ## # A tibble: 9,491 x 5 ## id amount type party receipt_date ## <chr> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <chr> ## 1 4924154.rcpt 20.0 Candidate REPUBLICAN 11/18/15 ## 2 5265339.rcpt 1000 Candidate DEMOCRAT 9/22/16 ## 3 4476891.rcpt 30.0 Political Committee <NA> 8/8/14 ## 4 4567569.rcpt 50.0 Political Committee <NA> 11/3/14 ## 5 2997493.rcpt 164 Candidate DEMOCRAT 8/30/10 ## 6 2241033.rcpt 50.0 Candidate DEMOCRAT 9/21/07 ## 7 4260975.rcpt 1.00 Political Committee <NA> 12/12/13 ## 8 2050846.rcpt 5.00 Candidate DEMOCRAT 4/17/08 ## 9 2426646.rcpt 50.0 Candidate DEMOCRAT 10/25/08 ## 10 1549664.rcpt 10.0 Candidate DEMOCRAT 7/24/06 ## # ... with 9,481 more rows
Select, create, and rename variables
select()keeps the named variables from the dataset- You can also remove variables from the dataset with
- - Nest functions within
select()usually do not work- Exception:
everything()
- Exception:
- Use
'``'for multi-word variables and variable names that begin with numbers
donor %>% select(id, amount, type, party, receipt_date) %>% select(-id) ## # A tibble: 9,491 x 4 ## amount type party receipt_date ## <dbl> <chr> <chr> <chr> ## 1 20.0 Candidate REPUBLICAN 11/18/15 ## 2 1000 Candidate DEMOCRAT 9/22/16 ## 3 30.0 Political Committee <NA> 8/8/14 ## 4 50.0 Political Committee <NA> 11/3/14 ## 5 164 Candidate DEMOCRAT 8/30/10 ## 6 50.0 Candidate DEMOCRAT 9/21/07 ## 7 1.00 Political Committee <NA> 12/12/13 ## 8 5.00 Candidate DEMOCRAT 4/17/08 ## 9 50.0 Candidate DEMOCRAT 10/25/08 ## 10 10.0 Candidate DEMOCRAT 7/24/06 ## # ... with 9,481 more rows
Select, create, and rename variables
select()keeps the named variables from the dataset- You can also remove variables from the dataset with
- - Nest functions within
select()usually do not work- Exception:
everything()
- Exception:
- Use
'``'for multi-word variables and variable names that begin with numbers
donor %>% select(id, amount, type, party, receipt_date) %>% select(id, receipt_date, everything()) ## # A tibble: 9,491 x 5 ## id receipt_date amount type party ## <chr> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <chr> ## 1 4924154.rcpt 11/18/15 20.0 Candidate REPUBLICAN ## 2 5265339.rcpt 9/22/16 1000 Candidate DEMOCRAT ## 3 4476891.rcpt 8/8/14 30.0 Political Committee <NA> ## 4 4567569.rcpt 11/3/14 50.0 Political Committee <NA> ## 5 2997493.rcpt 8/30/10 164 Candidate DEMOCRAT ## 6 2241033.rcpt 9/21/07 50.0 Candidate DEMOCRAT ## 7 4260975.rcpt 12/12/13 1.00 Political Committee <NA> ## 8 2050846.rcpt 4/17/08 5.00 Candidate DEMOCRAT ## 9 2426646.rcpt 10/25/08 50.0 Candidate DEMOCRAT ## 10 1549664.rcpt 7/24/06 10.0 Candidate DEMOCRAT ## # ... with 9,481 more rows
Select, create, and rename variables
mutate()creates variables- Create multiple variables in one go
- Use functions you already learned within
mutate()min(),max(),mean()as.character(),as.factor(),as.numeric()
- Use
ifelse()withinmutate()
x <- c(1, 2, 3) y <- c(4, 5, 1) ifelse(x > y, 'yes', 'no')
Select, create, and rename variables
mutate()creates variables- Create multiple variables in one go
- Use functions you already learned within
mutate()min(),max(),mean()as.character(),as.factor(),as.numeric()
- Use
ifelse()withinmutate()
x <- c(1, 2, 3) y <- c(4, 5, 1) ifelse(x > y, 'yes', 'no') ## [1] "no" "no" "yes"
Select, create, and rename variables
mutate()creates variables- Create multiple variables in one go
- Use functions you already learned within
mutate()min(),max(),mean()as.character(),as.factor(),as.numeric()
- Use
ifelse()withinmutate()
donor %>%
mutate(
amount_per_day = (amount / 365) %>% round(2)
, amount_perc_max = (amount / max(amount, na.rm = TRUE)) %>% round(2)
, amount_candidate = ifelse(type %in% 'Candidate', amount, NA)
, amount_committee = ifelse(type %in% 'Political Committee', amount, NA)
)
Select, create, and rename variables
donor %>%
mutate(
amount_per_day = (amount / 365) %>% round(2)
, amount_perc_max = (amount / max(amount, na.rm = TRUE)) %>% round(2)
, amount_candidate = ifelse(type %in% 'Candidate', amount, NA)
, amount_committee = ifelse(type %in% 'Political Committee', amount, NA)
) %>%
select(id, amount, amount_per_day, amount_perc_max
, amount_candidate, amount_committee) %>%
head(3) %>% as.data.frame()
## id amount amount_per_day amount_perc_max amount_candidate
## 1 4924154.rcpt 20 0.05 0.00 20
## 2 5265339.rcpt 1000 2.74 0.01 1000
## 3 4476891.rcpt 30 0.08 0.00 NA
## amount_committee
## 1 NA
## 2 NA
## 3 30
Select, create, and rename variables
Exercise - 5 minutes
- With the police dataset, create a variable called parking_violation
- Flag with a 1 all records that have a 'PARKING VIOLATIONS' value in event_clearance_subgroup.
All other records should have a 0
- Set incident_location to NA when the new variable parking_location is equal to 0
police %>%
mutate(
parking_violation = ifelse(event_clearance_subgroup %in% 'PARKING VIOLATIONS', 1, 0)
, incident_location = ifelse(parking_violation %in% 1, incident_location, NA)
) %>%
select(event_clearance_subgroup, parking_violation, incident_location) %>%
head()
Select, create, and rename variables
Exercise - 5 minutes
- With the police dataset, create a variable called parking_violation
- Flag with a 1 all records that have a 'PARKING VIOLATIONS' value in event_clearance_subgroup.
All other records should have a 0
- Set incident_location to NA when the new variable parking_location is equal to 0
police %>%
mutate(
parking_violation = ifelse(event_clearance_subgroup %in% 'PARKING VIOLATIONS', 1, 0)
, incident_location = ifelse(parking_violation %in% 1, incident_location, NA)
) %>%
select(event_clearance_subgroup, parking_violation, incident_location) %>%
head()
## # A tibble: 6 x 3
## event_clearance_subgroup parking_violation incident_location
## <chr> <dbl> <chr>
## 1 PARKING VIOLATIONS 1.00 (47.62256185, -122.325308913)
## 2 TRAFFIC RELATED CALLS 0 <NA>
## 3 TRAFFIC RELATED CALLS 0 <NA>
## 4 THEFT 0 <NA>
## 5 THEFT 0 <NA>
## 6 PARKING VIOLATIONS 1.00 (47.548520269, -122.38927419…
Select, create, and rename variables
transmute()=mutate()+select()
donor %>%
mutate(
amount_per_day = (amount / 365)
, amount_candidate = ifelse(type %in% 'Candidate', amount, NA)
, amount_committee = ifelse(type %in% 'Political Committee', amount, NA)
) %>%
select(amount_per_day, amount_candidate, amount_committee)
## # A tibble: 9,491 x 3
## amount_per_day amount_candidate amount_committee
## <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 0.0548 20.0 NA
## 2 2.74 1000 NA
## 3 0.0822 NA 30.0
## 4 0.137 NA 50.0
## 5 0.450 164 NA
## 6 0.137 50.0 NA
## 7 0.00274 NA 1.00
## 8 0.0137 5.00 NA
## 9 0.137 50.0 NA
## 10 0.0274 10.0 NA
## # ... with 9,481 more rows
Select, create, and rename variables
transmute()=mutate()+select()
donor %>%
transmute(
amount_per_day = (amount / 365)
, amount_candidate = ifelse(type %in% 'Candidate', amount, NA)
, amount_committee = ifelse(type %in% 'Political Committee', amount, NA)
)
## # A tibble: 9,491 x 3
## amount_per_day amount_candidate amount_committee
## <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 0.0548 20.0 NA
## 2 2.74 1000 NA
## 3 0.0822 NA 30.0
## 4 0.137 NA 50.0
## 5 0.450 164 NA
## 6 0.137 50.0 NA
## 7 0.00274 NA 1.00
## 8 0.0137 5.00 NA
## 9 0.137 50.0 NA
## 10 0.0274 10.0 NA
## # ... with 9,481 more rows
Select, create, and rename variables
- Keep unmanipulated variables too if you would like
donor %>%
transmute(
type
, amount
, amount_per_day = (amount / 365)
, amount_candidate = ifelse(type %in% 'Candidate', amount, NA)
, amount_committee = ifelse(type %in% 'Political Committee', amount, NA)
)
## # A tibble: 9,491 x 5
## type amount amount_per_day amount_candidate amount_com…
## <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 Candidate 20.0 0.0548 20.0 NA
## 2 Candidate 1000 2.74 1000 NA
## 3 Political Committee 30.0 0.0822 NA 30.0
## 4 Political Committee 50.0 0.137 NA 50.0
## 5 Candidate 164 0.450 164 NA
## 6 Candidate 50.0 0.137 50.0 NA
## 7 Political Committee 1.00 0.00274 NA 1.00
## 8 Candidate 5.00 0.0137 5.00 NA
## 9 Candidate 50.0 0.137 50.0 NA
## 10 Candidate 10.0 0.0274 10.0 NA
## # ... with 9,481 more rows
Select, create, and rename variables
rename()assigns a new name to an existing variable- Renaming is possible with
transmute()andmutate()as wellrename(): renames selected variables, keeps all other variablestransmute(): renames selected variables, drops all other variablesmutate(): creates new variables (with new names) and keeps originals
Exercise - 3 minutes
- Rename id as donor_id, first_name as donor_f_name, and last_name as donor_l_name with all three functions
Select, create, and rename variables
rename()assigns a new name to an existing variable- Renaming is possible with
transmute()andmutate()as wellrename(): renames selected variables, keeps all other variablestransmute(): renames selected variables, drops all other variablesmutate(): creates new variables (with new names) and keeps originals
donor %>%
rename(
donor_id = id
, donor_f_name = first_name
, donor_l_name = last_name
) %>%
as.data.frame() %>%
head(1)
## donor_id report_number origin filer_id type filer_name
## 1 4924154.rcpt 100670216 C3 MACED 592 Candidate MACEWEN DREW C
## donor_f_name middle_initial donor_l_name office
## 1 DREW C MACEWEN STATE REPRESENTATIVE
## legislative_district position party ballot_number for_or_against
## 1 35 2 REPUBLICAN NA <NA>
## jurisdiction jurisdiction_county jurisdiction_type
## 1 LEG DISTRICT 35 - HOUSE MASON Legislative
## election_year amount cash_or_in_kind receipt_date description memo
## 1 2016 20 Cash 11/18/15 <NA> <NA>
## primary_general code contributor_name contributor_address
## 1 Primary Individual MORSE DELANEY 410 E PICKERING RD.
## contributor_city contributor_state contributor_zip
## 1 SHELTON WA 98584
## contributor_occupation contributor_employer_name
## 1 <NA> <NA>
## contributor_employer_city contributor_employer_state
## 1 <NA> <NA>
## url
## 1 View report (http://web.pdc.wa.gov/rptimg/default.aspx?batchnumber=100670216)
## contributor_location receipt_year
## 1 (47.27572, -122.96448) 2015
Select, create, and rename variables
rename()assigns a new name to an existing variable- Renaming is possible with
transmute()andmutate()as wellrename(): renames selected variables, keeps all other variablestransmute(): renames selected variables, drops all other variablesmutate(): creates new variables (with new names) and keeps originals
donor %>%
transmute(
donor_id = id
, donor_f_name = first_name
, donor_l_name = last_name
)
## # A tibble: 9,491 x 3
## donor_id donor_f_name donor_l_name
## <chr> <chr> <chr>
## 1 4924154.rcpt DREW MACEWEN
## 2 5265339.rcpt SHERRY APPLETON
## 3 4476891.rcpt <NA> WA ST ASSN FOR JUSTICE JUSTICE FOR ALL
## 4 4567569.rcpt <NA> WA CONSERVATION VOTERS ACTION FUND
## 5 2997493.rcpt RAYMOND BUNK
## 6 2241033.rcpt CHRISTINE GREGOIRE
## 7 4260975.rcpt <NA> OFFICE & PROFESSIONAL EMPLOYEES LOCAL 8 PAC …
## 8 2050846.rcpt JUDITH OWENS
## 9 2426646.rcpt HANS DUNSHEE
## 10 1549664.rcpt KAREN FRASER
## # ... with 9,481 more rows
Select, create, and rename variables
rename()assigns a new name to an existing variable- Renaming is possible with
transmute()andmutate()as wellrename(): renames selected variables, keeps all other variablestransmute(): renames selected variables, drops all other variablesmutate(): creates new variables (with new names) and keeps originals
donor %>%
mutate(
donor_id = id
, donor_f_name = first_name
, donor_l_name = last_name
) %>%
select(donor_id, id, donor_f_name, first_name, donor_l_name, last_name) %>%
head(1)
## # A tibble: 1 x 6
## donor_id id donor_f_name first_name donor_l_name last_name
## <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr>
## 1 4924154.rcpt 4924154.rcpt DREW DREW MACEWEN MACEWEN
Exercise - 5 minutes
With
police, create a data frame that meets the following conditions- The dataset includes the variable
general_offense_numberwith no changes made to it - The dataset includes
initial_type_group NAvalues ininitial_type_groupare changed to'Unknown'- The dataset includes
incident_locationrenamed asevent_location
- The dataset includes the variable
police %>%
transmute(
general_offense_number
, initial_type_group = ifelse(initial_type_group %in% NA, 'Unknown', initial_type_group)
, event_location = incident_location
)
Exercise - 5 minutes
police %>%
transmute(
general_offense_number
, initial_type_group = ifelse(initial_type_group %in% NA, 'Unknown', initial_type_group)
, event_location = incident_location
) %>%
head()
## # A tibble: 6 x 3
## general_offense_number initial_type_group event_location
## <dbl> <chr> <chr>
## 1 2014401379 PARKING VIOLATIONS (47.62256185, -122.3253089…
## 2 2017134490 TRAFFIC RELATED CALLS (47.598347, -122.32376)
## 3 2015268887 TRAFFIC RELATED CALLS (47.620872118, -122.338467…
## 4 2010315966 Unknown (47.618242902, -122.338437…
## 5 201293086 Unknown (47.60925298, -122.3373387…
## 6 2010353531 Unknown (47.548520269, -122.389274…
Filter and reshape data frames
Filter and reshape data frames
- Use
filter()to subset your data - With
filter(), you tell R to exclude/include data that meet certain conditions - Operators for conditions
!,%in%,>,>=,<,<=,==
donor %>% filter(amount > 100) %>% select(id, amount) %>% head(2) ## # A tibble: 2 x 2 ## id amount ## <chr> <dbl> ## 1 5265339.rcpt 1000 ## 2 2997493.rcpt 164
donor %>% filter(amount <= 99) %>% select(id, amount) %>% head(2) ## # A tibble: 2 x 2 ## id amount ## <chr> <dbl> ## 1 4924154.rcpt 20.0 ## 2 4476891.rcpt 30.0
Filter and reshape data frames
- Use
filter()to subset your data - With
filter(), you tell R to exclude/include data that meet certain conditions - Operators for conditions
!,%in%,>,>=,<,<=,==
donor %>% filter(type %in% 'Candidate') %>% select(id, type) %>% head(2) ## # A tibble: 2 x 2 ## id type ## <chr> <chr> ## 1 4924154.rcpt Candidate ## 2 5265339.rcpt Candidate
donor %>% filter(! type %in% 'Candidate') %>% select(id, type) %>% head(2) ## # A tibble: 2 x 2 ## id type ## <chr> <chr> ## 1 4476891.rcpt Political Committee ## 2 4567569.rcpt Political Committee
Filter and reshape data frames
- You can stipulate multiple conditions with
filter()- Use
&for ‘and’ expressions - Use
|for ‘or’ expressions - If there are many conditions, wrap conditions in
()or use more than onefilter() - If you want to filter on multiple vaues, use
c()
- Use
donor %>% filter(amount > 100 & type %in% 'Candidate') %>% select(id, amount, type) %>% head(2) ## # A tibble: 2 x 3 ## id amount type ## <chr> <dbl> <chr> ## 1 5265339.rcpt 1000 Candidate ## 2 2997493.rcpt 164 Candidate
Filter and reshape data frames
- You can stipulate multiple conditions with
filter()- Use
&for ‘and’ expressions - Use
|for ‘or’ expressions - If there are many conditions, wrap conditions in
()or use more than onefilter() - If you want to filter on multiple vaues, use
c()
- Use
donor %>% filter(amount > 100 | type %in% 'Candidate') %>% select(id, amount, type) %>% head(2) ## # A tibble: 2 x 3 ## id amount type ## <chr> <dbl> <chr> ## 1 4924154.rcpt 20.0 Candidate ## 2 5265339.rcpt 1000 Candidate
Filter and reshape data frames
- You can stipulate multiple conditions with
filter()- Use
&for ‘and’ expressions - Use
|for ‘or’ expressions - If there are many conditions, wrap conditions in
()or use more than onefilter() - If you want to filter on multiple vaues, use
c()
- Use
donor %>%
filter(
(amount > 100 & type %in% 'Candidate') |
(amount <= 99 & type %in% 'Political Committee')
) %>%
select(id, amount, type) %>%
head()
## # A tibble: 6 x 3
## id amount type
## <chr> <dbl> <chr>
## 1 5265339.rcpt 1000 Candidate
## 2 4476891.rcpt 30.0 Political Committee
## 3 4567569.rcpt 50.0 Political Committee
## 4 2997493.rcpt 164 Candidate
## 5 4260975.rcpt 1.00 Political Committee
## 6 3945799.rcpt 500 Candidate
Filter and reshape data frames
- You can stipulate multiple conditions with
filter()- Use
&for ‘and’ expressions - Use
|for ‘or’ expressions - If there are many conditions, wrap conditions in
()or use more than onefilter() - If you want to filter on multiple vaues, use
c()
- Use
donor %>%
filter(contributor_name %in% c('BEZOS JACKIE', 'COSTCO')) %>%
select(contributor_name, amount, type)
## # A tibble: 3 x 3
## contributor_name amount type
## <chr> <dbl> <chr>
## 1 BEZOS JACKIE 100000 Political Committee
## 2 COSTCO 71.8 Candidate
## 3 COSTCO 95000 Political Committee
Filter and reshape data frames
- Other functions for subsetting your data
head()tail()sample_n()
donor %>% sample_n(3) %>% select(contributor_name, type, amount) ## # A tibble: 3 x 3 ## contributor_name type amount ## <chr> <chr> <dbl> ## 1 LIBERTY SHORES ASSISTED LIVING Political Committee 252 ## 2 SPENCER WILLIAM A. Candidate 1400 ## 3 SELTZER LINDA Candidate 150
donor %>% sample_n(3) %>% select(contributor_name, type, amount) ## # A tibble: 3 x 3 ## contributor_name type amount ## <chr> <chr> <dbl> ## 1 RETAIL ACTION COUNCIL Candidate 900 ## 2 SCHAADT LEONARD C Political Committee 50.0 ## 3 FENDER CARL Political Committee 5.00
Filter and reshape data frames
Exercise - 10 minutes
- Produce a dataset that meets these conditions
- Contains values in
partynot equal to ‘REPUBLICAN’ or ‘DEMOCRAT’ - Contains no donations prior to January 1, 2017
- Contains a variable called
candidate_flag. This variable should flag with a1observations that have atypeequal toCandidate - Contains 4 variables in total in the following order:
id,candidate_flag,party,receipt_date
- Contains values in
- Determine how many records meet the above filtering conditions
- Hint
- Convert
receipt_dateinto date variable (currently a character variable) - Use
lubridate::mdy() - Download the
lubridatelibrary if it does not load successfully - Dates will convert to the following format: yyyy-mm-dd
- Put dates between quotation marks when filter:
'yyyy-mm-dd'
- Convert
Filter and reshape data frames
- Hint
donor %>% transmute(receipt_date = receipt_date %>% mdy()) %>% filter(receipt_date >= '2017-01-01') %>%
Filter and reshape data frames
donor %>%
transmute(
id
, candidate_flag = ifelse(type %in% 'Candidate', 1, 0)
, party
, receipt_date = receipt_date %>% mdy()
) %>%
filter(
! party %in% c('REPUBLICAN', 'DEMOCRAT') &
receipt_date >= '2017-01-01'
) %>%
sample_n(4)
## # A tibble: 4 x 4
## id candidate_flag party receipt_date
## <chr> <dbl> <chr> <date>
## 1 5500784.rcpt 0 <NA> 2017-05-10
## 2 5619997.rcpt 0 <NA> 2017-08-31
## 3 5532757.rcpt 1.00 NON PARTISAN 2017-06-11
## 4 5549542.rcpt 1.00 NON PARTISAN 2017-06-30
Filter and reshape data frames
donor %>%
filter(
! party %in% c('REPUBLICAN', 'DEMOCRAT') &
receipt_date >= '2017-01-01'
) %>%
nrow()
## [1] 3976
Filter and reshape data frames
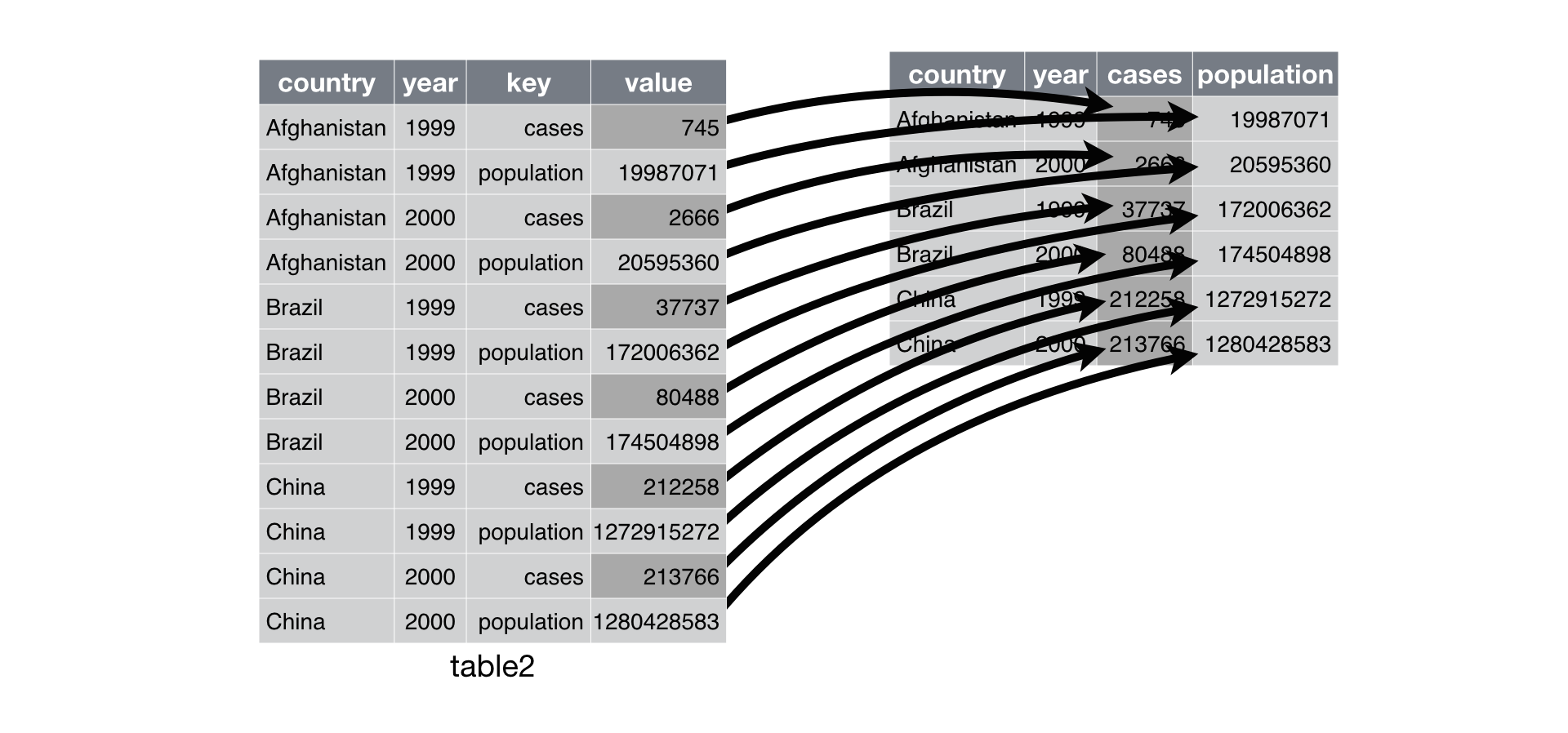
gather()andspread()are the functions we use to reshape data- Reshape means to convert…
- Columns into rows (with
gather()) - Rows into columns (with
spread())
- Columns into rows (with
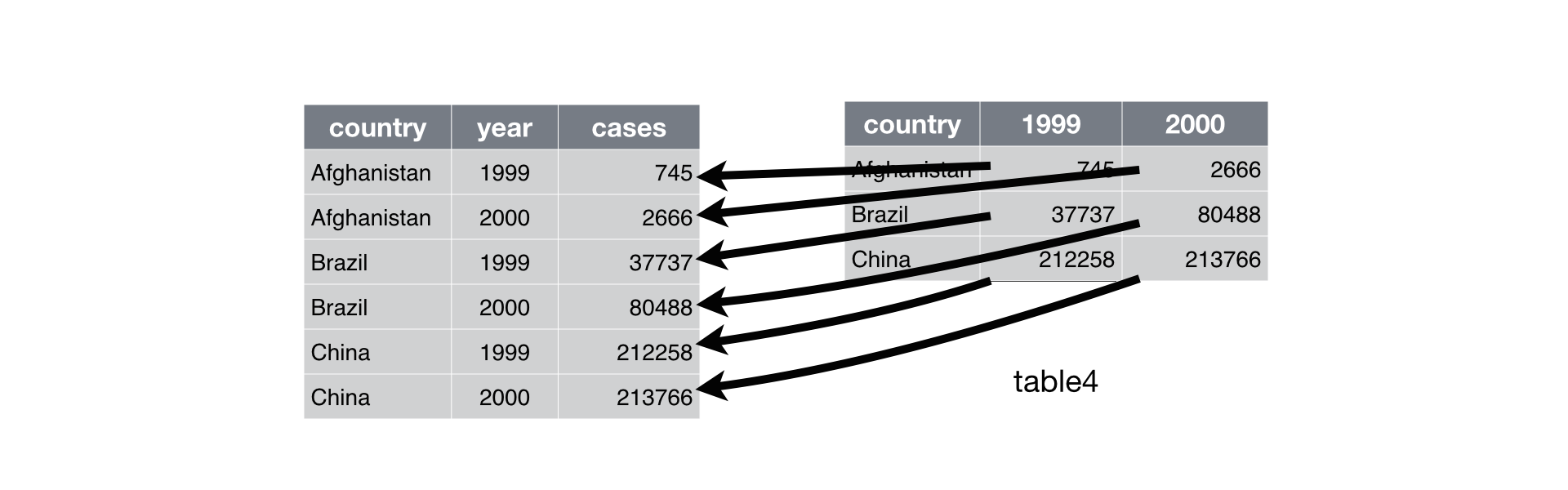
Filter and reshape data frames
gather()andspread()are the functions we use to reshape data- Reshape means to convert…
- Columns into rows (with
gather()) - Rows into columns (with
spread())
- Columns into rows (with
Filter and reshape data frames
gather()- Convert columns into rows
- Arguments
- Data frame (of course)
- Name of column for column names
- Name of column for values in columns
- Which columns you want turn into rows
donor %>% gather(column_name, year, c(receipt_year, election_year))
Filter and reshape data frames
gather()- Convert columns into rows
- Arguments
- Data frame (of course)
- Name of column for column names
- Name of column for values in columns
- Which columns you want turn into rows
donor %>% gather(column_name, year, c(19, 38))
Filter and reshape data frames
donor %>% gather(column_name, year, c(receipt_year, election_year)) %>% select(contributor_name, column_name, year) %>% head(3) ## # A tibble: 3 x 3 ## contributor_name column_name year ## <chr> <chr> <dbl> ## 1 MORSE DELANEY receipt_year 2015 ## 2 ATU LEGISLATIVE COUNCIL OF WASHINGTON STATE receipt_year 2016 ## 3 GIERTH RICHARD L MR. receipt_year 2014

Filter and reshape data frames
spread()- Convert rows into columns
- Arguments
- Data frame (of course)
- Name of column that contains the names of the new columns
- Name of columns that contains the values of the new columns
donor %>% spread(receipt_year, amount)
Filter and reshape data frames
donor %>%
spread(receipt_year, amount) %>%
filter(contributor_name %in% c('BEZOS JACKIE', 'COSTCO')) %>%
select(26, 37:50) %>% as.data.frame()
## contributor_name 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013
## 1 BEZOS JACKIE NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA 1e+05 NA
## 2 COSTCO NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA
## 3 COSTCO NA NA NA NA NA NA 95000 NA NA NA
## 2014 2015 2016 2017
## 1 NA NA NA NA
## 2 NA NA 71.81 NA
## 3 NA NA NA NA

Filter and reshape data frames
Exercise #1 - 3 minutes
- With
police, usegather()to convertevent_clearance_group,event_clearance_subgroup,initial_type_group, andinitial_type_subgroupcolumns into rows - Name the two new columns whatever you would like
Exercise #2 - 3 minutes
- With
donor, usespread()to turntypevalues into new columns - The values in the new
typecolumns should beamountvalues
Filter and reshape data frames
Exercise #1 - 3 minutes
- With
police, usegather()to convertevent_clearance_group,event_clearance_subgroup,initial_type_group, andinitial_type_subgroupcolumns into rows - Name the two new columns whatever you would like
police %>%
gather(group, value, c(event_clearance_group, event_clearance_subgroup
, initial_type_group, initial_type_subgroup))
Filter and reshape data frames
Exercise #1 - 3 minutes
- With
police, usegather()to convertevent_clearance_group,event_clearance_subgroup,initial_type_group, andinitial_type_subgroupcolumns into rows - Name the two new columns whatever you would like
police %>%
gather(group, value, c(event_clearance_group, event_clearance_subgroup
, initial_type_group, initial_type_subgroup)) %>%
select(general_offense_number, group, value) %>%
sample_n(8)
## # A tibble: 8 x 3
## general_offense_number group value
## <dbl> <chr> <chr>
## 1 201738506 event_clearance_group SUSPICIOUS CIRCUMSTANCES
## 2 2012184439 event_clearance_group ANIMAL COMPLAINTS
## 3 2015308086 event_clearance_group SUSPICIOUS CIRCUMSTANCES
## 4 2015416217 event_clearance_group FALSE ALACAD
## 5 2016269191 event_clearance_subgroup SUSPICIOUS CIRCUMSTANCES
## 6 2014408211 event_clearance_group SUSPICIOUS CIRCUMSTANCES
## 7 2015368511 event_clearance_subgroup TRAFFIC RELATED CALLS
## 8 2012287369 initial_type_subgroup <NA>
Filter and reshape data frames
Exercise #2 - 3 minutes
- With
donor, usespread()to maketypevalues new column names - The values in the new
typecolumns should beamountvalues
donor %>% spread(type, amount)
Filter and reshape data frames
Exercise #2 - 3 minutes
- With
donor, usespread()to maketypevalues new column names - The values in the new
typecolumns should beamountvalues
donor %>% spread(type, amount) %>% select(id, `Political Committee`, `Candidate`) %>% head() ## # A tibble: 6 x 3 ## id `Political Committee` Candidate ## <chr> <dbl> <dbl> ## 1 4924154.rcpt NA 20.0 ## 2 5265339.rcpt NA 1000 ## 3 4476891.rcpt 30.0 NA ## 4 4567569.rcpt 50.0 NA ## 5 2997493.rcpt NA 164 ## 6 2241033.rcpt NA 50.0
Aggregate data with group_by() and summarise()
What you can do with group_by() and summarise()
- Count, sum, average, and identify max and min values
- Example questions you could answer
- In
donor, whichtypereceived the more money in donations from'REPUBLICAN'? - In
donor, whichtypereceived the largest number of donations and how much did thetypereceive? - In
police, of'BURGLARY'values inevent_clearance_groupwhichevent_clearance_subgroupvalue has the fewest incidences? - In
donor, what is the largest average donationamountforcontributor_state?
- In
How you use group_by() and summarise() to aggregate data
- In
group_by(), list the variables by which you want to aggregate data - In
summarise(), create a variable and define the variable with an aggregation function - Use
%>%to ‘link’group_by()andsummarise() - Aggregation functions
n(),n_distinct(),sum(),mean(),max(),min(), etc.
Example
In donor, which type received the more money in donations from 'REPUBLICAN'?
donor %>% group_by(type, party) %>% summarise(dollars = sum(amount, na.rm = TRUE))
How you use group_by() and summarise() to aggregate data
Example
In donor, which type received the more money in donations from 'REPUBLICAN'?
donor %>% group_by(type, party) %>% summarise(dollars = sum(amount, na.rm = TRUE)) ## # A tibble: 7 x 3 ## # Groups: type [?] ## type party dollars ## <chr> <chr> <dbl> ## 1 Candidate DEMOCRAT 311690 ## 2 Candidate INDEPENDENT 467 ## 3 Candidate NON PARTISAN 206196 ## 4 Candidate NONE 6465 ## 5 Candidate OTHER 25859 ## 6 Candidate REPUBLICAN 313540 ## 7 Political Committee <NA> 1563098
How you use group_by() and summarise() to aggregate data
Example
In donor, which type received the largest number of donations and how much did the type receive?
donor %>%
group_by(type) %>%
summarise(
donations = n()
, total_amount = sum(amount, na.rm = TRUE)
)
## # A tibble: 2 x 3
## type donations total_amount
## <chr> <int> <dbl>
## 1 Candidate 3680 864217
## 2 Political Committee 5811 1563098
How you use group_by() and summarise() to aggregate data
Exercise #1 - 3 minutes
In police, of 'BURGLARY' values in event_clearance_group which event_clearance_subgroup value has the fewest incidences?
Exercise #2 - 3 minutes
In donor, what is the largest average donation amount for contributor_state?
How you use group_by() and summarise() to aggregate data
Exercise #1 - 3 minutes
In police, of 'BURGLARY' values in event_clearance_group which event_clearance_subgroup value has the fewest incidences?
police %>% group_by(event_clearance_group, event_clearance_subgroup) %>% summarise(incidence = n())
How you use group_by() and summarise() to aggregate data
Exercise #1 - 3 minutes
In police, of 'BURGLARY' values in event_clearance_group which event_clearance_subgroup value has the fewest incidences?
police %>% group_by(event_clearance_group, event_clearance_subgroup) %>% summarise(incidence = n()) %>% filter(event_clearance_group %in% 'BURGLARY') ## # A tibble: 2 x 3 ## # Groups: event_clearance_group [1] ## event_clearance_group event_clearance_subgroup incidence ## <chr> <chr> <int> ## 1 BURGLARY COMMERCIAL BURGLARIES 94 ## 2 BURGLARY RESIDENTIAL BURGLARIES 218
How you use group_by() and summarise() to aggregate data
Exercise #2 - 3 minutes
In donor, what is the largest average donation amount for contributor_state?
donor %>% group_by(contributor_state) %>% summarise(avg_donation = mean(amount, na.rm = TRUE))
How you use group_by() and summarise() to aggregate data
Exercise #2 - 3 minutes
In donor, what is the largest average donation amount for contributor_state?
donor %>% group_by(contributor_state) %>% summarise(avg_donation = mean(amount, na.rm = TRUE)) %>% arrange(desc(avg_donation)) ## # A tibble: 43 x 2 ## contributor_state avg_donation ## <chr> <dbl> ## 1 <NA> 7965 ## 2 DC 6892 ## 3 WI 3596 ## 4 MT 1713 ## 5 CA 894 ## 6 KS 850 ## 7 ND 518 ## 8 VA 412 ## 9 NM 400 ## 10 MO 398 ## # ... with 33 more rows
Exercise - 15 minutes
- Create an output that reports counts of
initial_type_groupbydistrict_sector - Coerce the variables used in this exercise as character variables
- The
initial_type_groupcounts should only be for observations with a'DISTURBANCES'value in theevent_clearance_group - Change
NAinitial_type_groupvalues to'Unknown' Export the output to a .csv file with
write_csv()- Questions
- How many
'Unknown'values are indistrict_sector'W'? - How many
'ROAD RAGE'values are indistrict_sector'L'?
- How many
Exercise - 15 minutes
- Hint
'lines of code for processing data' %>%
write_csv('tidyverse_exercise_output.csv')
Exercise - 15 minutes
police %>%
transmute(
initial_type_group = initial_type_group %>% as.character()
, district_sector = district_sector %>% as.character()
, event_clearance_group = event_clearance_group %>% as.character()
) %>%
mutate(
initial_type_group = ifelse(initial_type_group %in% NA, 'Unknown', initial_type_group)
) %>%
filter(event_clearance_group %in% 'DISTURBANCES') %>%
group_by(initial_type_group, district_sector) %>%
summarise(n = n()) %>%
write_csv('tidyverse_exercise_output.csv')
Exercise - 15 minutes
police %>%
transmute(
initial_type_group = initial_type_group %>% as.character()
, district_sector = district_sector %>% as.character()
, event_clearance_group = event_clearance_group %>% as.character()
) %>%
mutate(
initial_type_group = ifelse(initial_type_group %in% NA, 'Unknown', initial_type_group)
) %>%
filter(event_clearance_group %in% 'DISTURBANCES') %>%
group_by(initial_type_group, district_sector) %>%
summarise(n = n()) %>%
filter(
(initial_type_group %in% 'Unknown' & district_sector %in% 'W') |
(initial_type_group %in% 'ROAD RAGE' & district_sector %in% 'L')
)
## # A tibble: 2 x 3
## # Groups: initial_type_group [2]
## initial_type_group district_sector n
## <chr> <chr> <int>
## 1 ROAD RAGE L 2
## 2 Unknown W 28
Exercise - 10 minutes
- Create an output that tells the number of
'FRAUD CALLS'and'HARBOR CALLS'in theevent_clearance_groupandinitial_type_groupvariables - To make it easier on yourself
gather()event_clearance_groupandinitial_type_group - Make sure you count the incidences using
group_by()andsummarise() - Export the output to a .csv file with
write_csv()
police %>%
gather(event_group, event_type, c(event_clearance_group, initial_type_group)) %>%
filter(event_type %in% c('FRAUD CALLS', 'HARBOR CALLS')) %>%
group_by(event_group, event_type) %>%
summarise(n = n()) %>%
write_csv('calls_incidences.csv')
Exercise - 10 minutes
police %>%
gather(event_group, event_type, c(event_clearance_group, initial_type_group)) %>%
filter(event_type %in% c('FRAUD CALLS', 'HARBOR CALLS')) %>%
group_by(event_group, event_type) %>%
summarise(n = n())
## # A tibble: 4 x 3
## # Groups: event_group [?]
## event_group event_type n
## <chr> <chr> <int>
## 1 event_clearance_group FRAUD CALLS 120
## 2 event_clearance_group HARBOR CALLS 5
## 3 initial_type_group FRAUD CALLS 77
## 4 initial_type_group HARBOR CALLS 5