Econ 107 LAB session: Week2
Ran Wang
Several Important Things
In-class assignment 1 in the next week.
Do-file + Results (via Microsoft Words)
You can use your own computer in class
No make-up assignment
Linear Regression
Data: X,Y
\[ X=(x_1,x_2,...,x_n) \] \[ Y=(y_1,y_2,...,y_n) \]
Linear Regression
Model:
\[ y=\beta_0+\beta_1x+u \]
Linear Regression
Estimate: OLS
\[ Min:\sum_{i=1}^{n}u_i^2=\sum_{i=1}^{n}(y_i-\beta_0-\beta_1x_i)^2 \] \[ \rightarrow \hat{\beta}_0,\hat{\beta}_1 \]
Confidence Interval (95%):
\[ \hat{\beta}\pm t_{1.96}\times standard~error \]
Linear Regression
Hypothesis Test:
\[ H_0:\hat{\beta}=0(t\leq c) \] \[ H_1:\hat{\beta}\neq0(t>c) \]
\[ t_{\beta}=\frac{\hat{\beta}-0}{stantdard~error} \]
\[ standard~error=\hat{\sigma}/\sqrt{n} \]
\( p \) value:
\[ P(x>t) \]
where \( x\sim t-dist \)
Linear Regression

Linear Regression
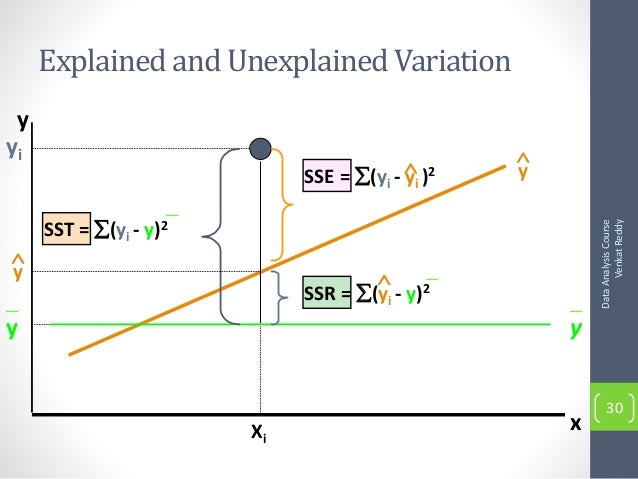
Goodness of Fit:\( R^2 \)
\[ R^2=\frac{SS_{reg}}{SS_{tot}} \]
where \( SS_{tot}=\sum_{i}^{n}(y_i-\bar{y})^2 \),\( SS_{reg}=\sum_{i}^{n}(\hat{y}_i-\bar{y})^2 \).
Intuition: \( R^2=\frac{explained~variance}{total~variation} \)
Linear Regression
Goodness of Fit:\( R^2 \)
Question Part
Data: CPS08
E4.1: CPS08 contains data on full-time, full-year workers, age 25-34, with a high school diploma or BA/BS.
( a ) Run a regression of average hourly earning (AHE) on age (Age): What is the estimated intercept? What is the estimated slope? Use the estimated regression to answer this question: How much do earnings increase as workers age by 1 year?
( b ) Bob is a 26-year-old worker. Predict Bobs earnings using the estimated regression. Alexis is a 30-year-old worker. Predict Alexisearnings using the estimated regression.
( c ) Does age account for a large fraction of the variance in earnings across individuals? Explain.
Question Part
Data: CPS08
E5.1: Run a regression of (AHE) on (Age) and carry out the following exercises.
( a ) Is the estimated regression slope coefficient statistically signicant? That is, can you reject the null hypothesis, H0:1 = 0 versus a two-sided alternative at 10%, 5% or 1% signicance level? What is the pvalue associated with the coefficient tstatistic?
( b ) Construct a 95% condence interval for the slope coefficient.
( c ) Repeat (a) using only the data for high school graduates.
( d ) Repeat (a) using only the data for college graduates.
( e ) Is the effect of age on earnings different for high school graduates than for college graduates? Explain.