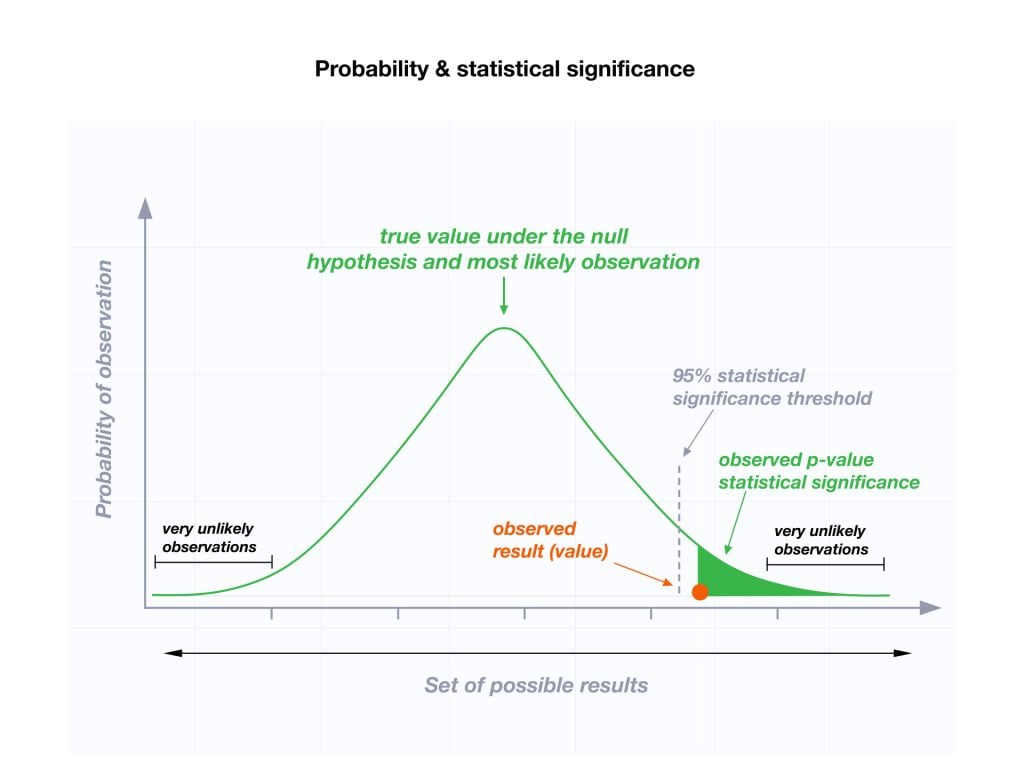
The p-value is a number, calculated from a statistical test, that describes how likely you are to have found a particular set of observations if the null hypothesis were true.
P-values are used in hypothesis testing to help decide whether to reject the null hypothesis. The smaller the p-value, the more likely you are to reject the null hypothesis.
Null hypothesis: assuming a statement about a population is true. For most tests, the null hypothesis is that there is no relationship between your variables of interest or that there is no difference among groups.
Alternative hypothesis: something else about that population is true. For most tests, the alternative hypothesis is that there is a relationship between your variables of interest or that there is a difference among groups.